Figure 1. TGF-β signaling in nickel-induced EMT.
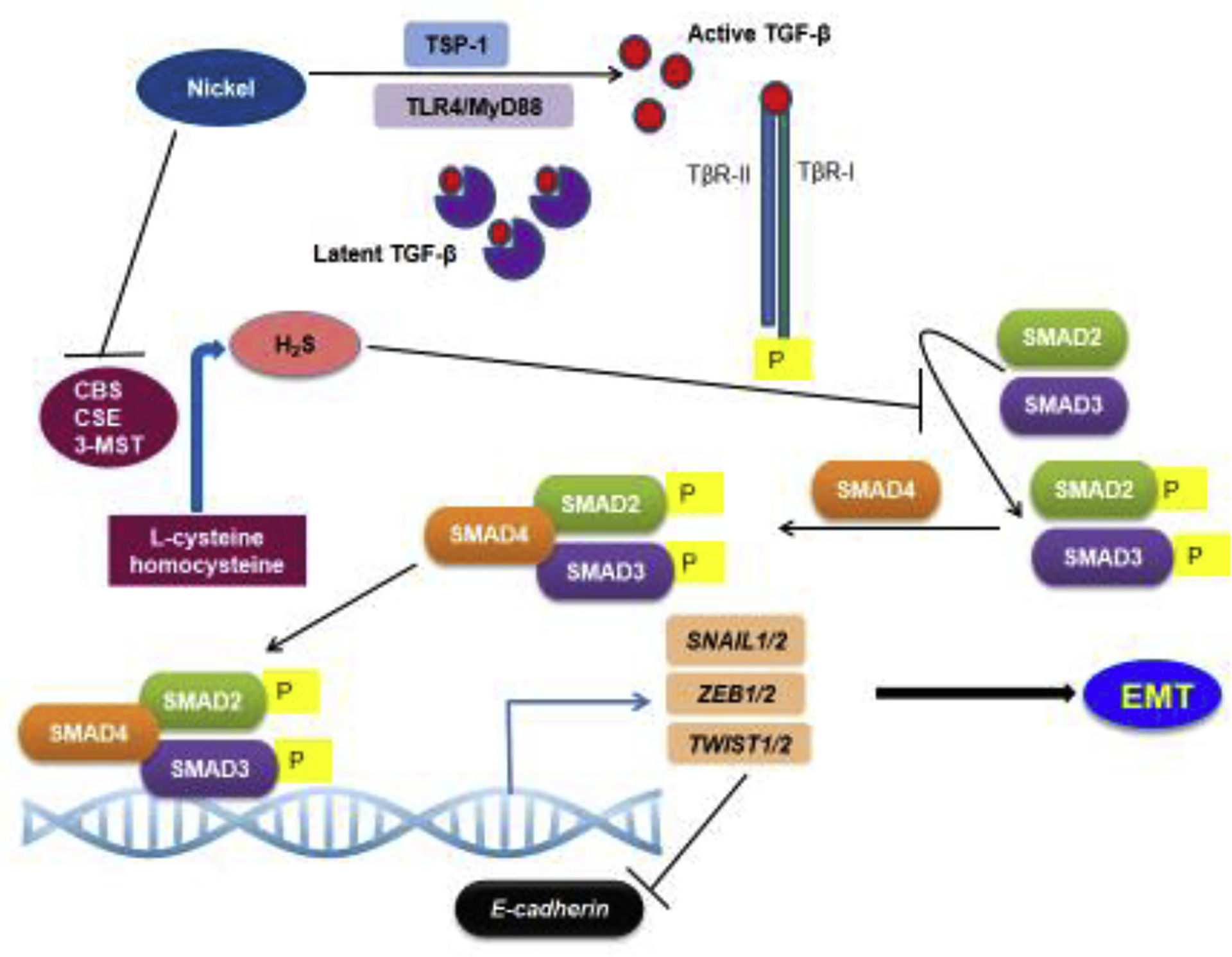
During TGF-β signaling, the active TGF-β binds the TGF-β receptors TGF-βR1 and TGF-βRII. The activation of the TGF-β receptor complex results in phosphorylation of the SMAD proteins, which then translocate to the nucleus and regulate target gene expression. Nickel exposure could activate TGF-β signaling via multiple mechanisms, including TLR4 signaling, TSP-1 upregulation and inhibition of H2S production. Nickel exposure induces TLR4 signaling. which has been shown to enhance TGF-β signaling. The extracellular matrix protein, TSP-1, an important activator of latent TGF-β, is one of the highest upregulated genes in the lungs of mice exposed to nickel, suggesting its role in nickel-induced TGF-β signaling. H2S is an important negative regulator of TGF-β signaling. Nickel exposure promoted TGF-β signaling by downregulating the enzymes involved in H2S production, CBS, CSE and 3MST, thereby increasing protein levels of TGF-β1 and phosphorylated SMAD2 and SMAD3.
