Figure 6. Characterization of the Kirrel3 Q128A mouse.
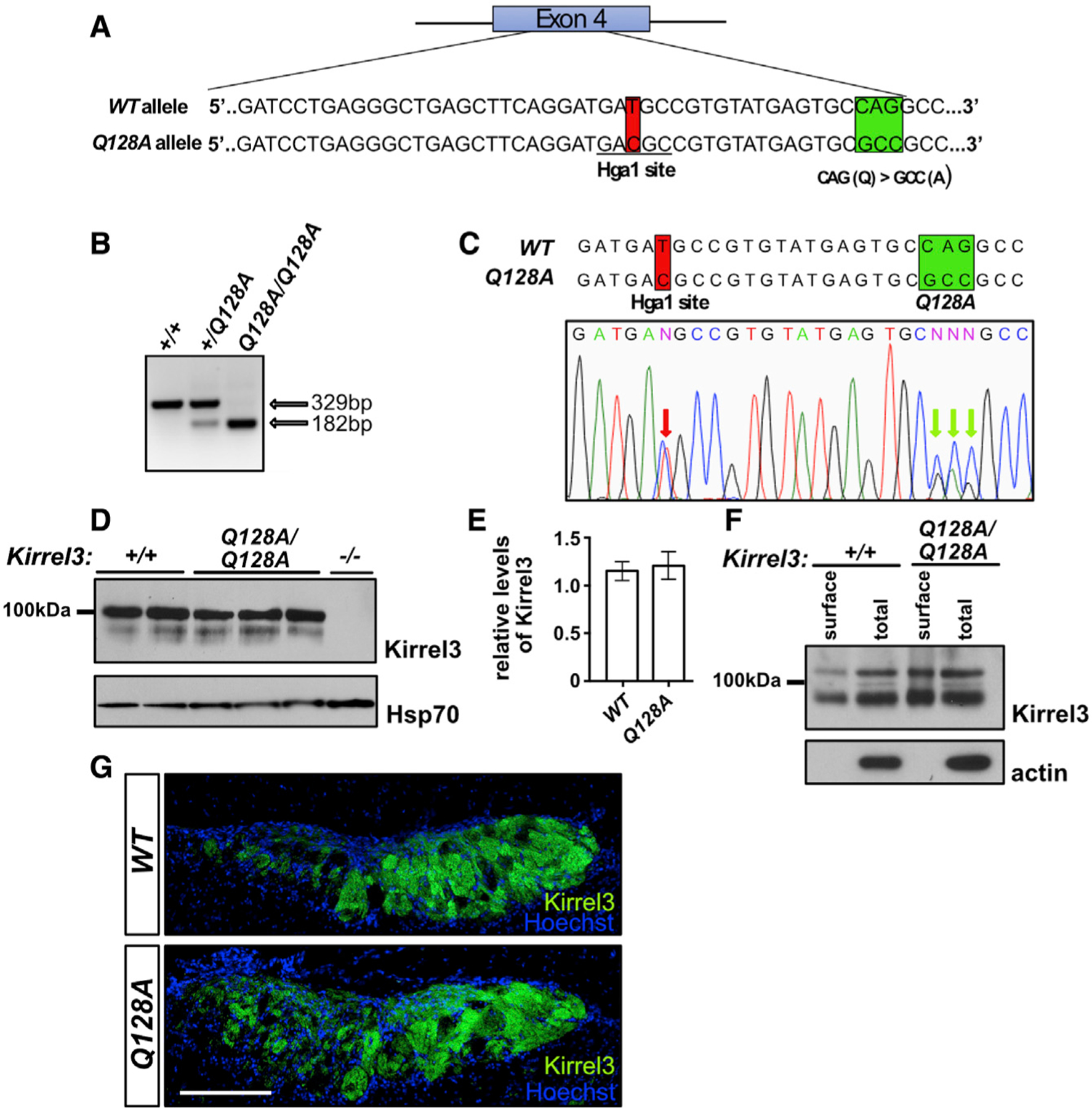
(A) Diagram of the generation of the Kirrel3 Q128A mouse. Mice carrying a modified Kirrel3 allele containing mutations that modify amino acid 128 from a Q to an A, as well as a silent mutation introducing an HgaI restriction enzyme cutting site for genotyping purposes, were generated. Green square: Q to A mutations; red square: mutation creating an HgaI restriction site.
(B and C) Identification of the Kirrel3 Q128A allele by restriction enzyme digest and DNA sequencing. Digestion with HgaI (B) and DNA sequencing (C) of a PCR fragment from exon 4 of the Kirrel3 allele demonstrate the presence of the newly introduced HgaI restriction site. DNA sequencing also reveals the presence of the three nucleotide substitutions resulting in the Q-to-A amino acid substitution in a Kirrel3+/Q128A mouse. The red arrows in the electropherogram in (C) indicate the overlapping peaks caused by the nucleotide substitutions in one of the Kirrel3 alleles.
(D and E) Quantification of Kirrel3 protein by western blot of brain lysate collected from Kirrel3+/+ and Kirrel3Q128A/Q128A mice shows that similar levels of Kirrel3 and Kirrel3 Q128A levels are expressed in the brain of these mice, respectively. Data were analyzed using unpaired t test; n = 3 for Kirrel3+/+ and n = 4 for Kirrel3Q128A/Q128A mice.
(F) Surface membrane distribution of Kirrel3 Q128A in acute brain slices. Western blots of acute brain slice lysate collected from Kirrel3+/+ and Kirrel3Q128A/Q128A mice following incubation with biotin and isolation of surface proteins by batch streptavidin chromatography. Both Kirrel3 and Kirrel3 Q128A are distributed to the cell surface.
(G) Immunohistochemistry on sagittal sections of the AOB from Kirrel3+/+ and Kirrel3Q128A/Q128A adult mice labeled with antibodies against Kirrel3 and Hoechst. The Kirrel3 and Kirrel3 Q128 proteins can be detected in subsets of glomeruli in both the anterior and posterior regions of the AOB in Kirrel3+/+ and Kirrel3Q128A/Q128A mice, respectively. The scale bar represents 200 mm. See also Figure S6.
