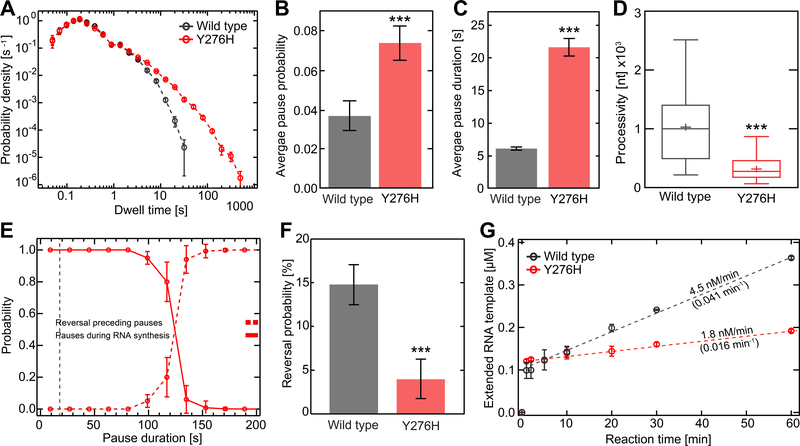
Figure 3. EV-A71 Y276H RdRp variant is impaired for copy-back RNA synthesis.
(A) Superimposed dwell-time distributions for EV-A71 Y276H RdRp (red) and WT (black) RdRp. The dwell times used for the construction of the distributions are the time needed for the RdRps to synthesize four consecutive nucleotides. The Y276H variant exhibits a broad increase in the probability and duration of long pauses compared to WT. The error bars (AVG±SD) result from bootstrapping with 1,000 iterations. (B-D) Quantification of the data in panel (A). In comparison to WT RdRp, the Y276H variant shows a significant increase in (B) average pausing probability (±SD) and (C) average apparent pause duration (±SEM). The processivity (D) is significantly decreased for the Y267H RdRp variant compared to WT. (E) The probability of observing pauses of specified durations during RNA synthesis (red line) co-plotted with the probability of observing reversals (red dashed line); the crossover point amounts to ~123 s. (F) The Y276H RdRp (red) variant causes significantly fewer reversal events (AVG±SD) than WT RdRp (grey). (G) In vitro bulk RNA synthesis assay results (AVG±SD; n = 3 repetitions) showing the amount of extended Sym/SubU template for EV-A71 WT and Y276H RdRp over time. Dashed lines represent linear regressions fitted to the data, revealing significantly lower approximated rates of RNA extension (values above the dashed lines) and turnover (values below the dashed lines; unit: RNA min−1 RdRp−1) for the Y276H RdRp variant compared to WT. Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired, two-tailed t-tests (significance level p: *** ≤ 0.001).