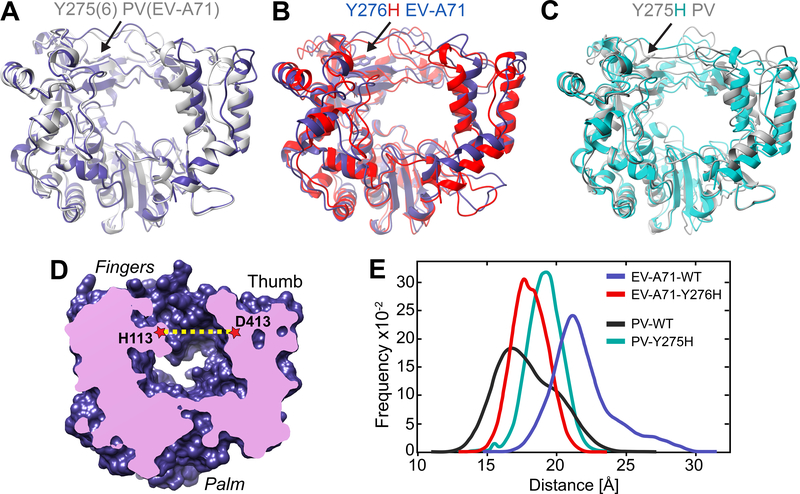
Figure 5. RNA-duplex channel dimensions and conformational dynamics of EV-A71 and PV RdRps.
(A) Superimposed crystal structures of EV-A71 WT (blue) and PV WT (grey) shown as cartoons. (B) Superimposed crystal structures of EV-A71 WT (blue) and major conformation of its Y276H mutant (red). (C) Superimposed crystal structures of PV WT (grey) and major conformation of its Y275H mutant (cyan). The major conformation of the Y275(6)H mutants resulted from MD simulations. (D) Cut-through volume rendering of EV-A71 WT crystal structure (PDB 3N6L), where the RNA duplex channel can be observed in the center of the structure. The channel width was assessed by measuring the distance between His-113 at the fingers and Asp-413 at the thumb domains in EV-A71, or their equivalent residues Ser-112 and Asp-412 in the PV WT crystal structure (PDB 1RA6). (E) RNA duplex channel widths measured for EV-A71 WT (blue) and PV WT (black) from their crystal structures, and from MD simulations for the EV-A71 Y276H variant (red).