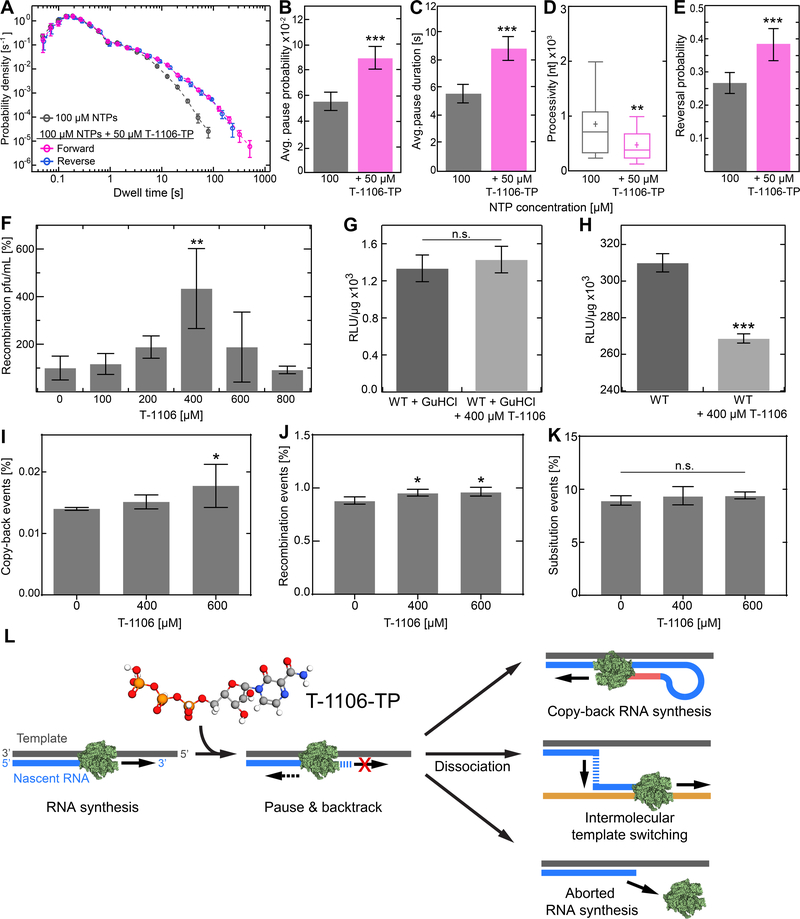
Figure 6. Pyrazine carboxymide T-1106 induces an increase in intra- and intermolecular template switching in vitro and in cell.
(A) Superimposed dwell-time distributions of EV-A71 RdRp forward RNA synthesis activity in the presence (magenta) or absence (grey) of the nucleotide analogue T-1106-TP. The reverse RNA synthesis dwell-time distribution in absence of T-1106-TP (blue) is superimposed. The dwell-time window was set to 4 nt, and the error bars (±SD) result from bootstrapping with 1,000 iterations. (B-E) The addition of T-1106-TP changed significantly the pausing behavior of WT RdRp, exhibiting significantly increased (B) pausing probability (±SD) and (C) average pause duration (±SEM), which led to a (D) significantly decreased in RNA synthesis processivity, and (E) vastly increased copy-back RNA synthesis probability. (F) Cell-based recombination assays conducted in presence of different concentrations of T-1106. Relative viable WT recombinant yield, normalized as a percentage of a carrier (DMSO) treated control (AVG ±SD; N = 3 replicates for each condition). Calculated IC50 amounts to 340±140 μM T-1106; the HeLa cell toxicity (CC50) of T-1106 was found to be >2 mM (Dulin et al., 2017). (G, H) EV-A71 donor translation (G) and replication (H) efficiency (AVG±SD) for WT RdRp. (I-K) The frequency of identified (I) copy-back RNA synthesis and (J) homologous recombination events, extracted from RNAseq, were significantly increased upon T-1106 addition, while (K) no change in mutation occurrence within the EV-A71 genome was observed. (L) Model mechanism of pyrazine carboxymide nucleotide analogue causing stall in RNA synthesis leading to copy-back RNA synthesis, intermolecular template switching, or abortive genome synthesis by RdRp dissociation. Statistical analyses were performed using ANOVA with comparative Tukey post-hoc test (significance levels α: *** = 0.001; ** = 0.01; * = 0.05; n.s. = non-significant), and unpaired, two-tailed t-tests (significance level p: *** ≤ 0.001). See also Figures S3 and S4.