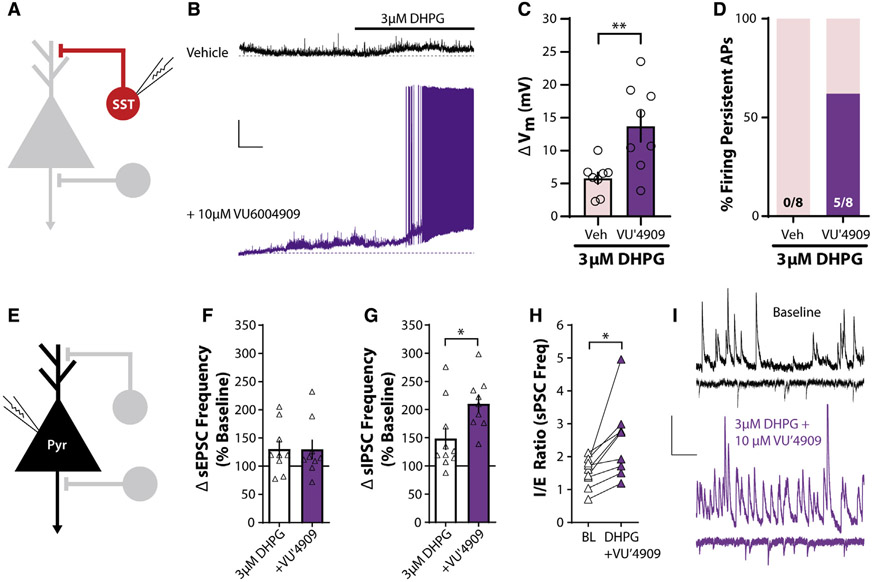
Figure 4. The mGlu1 PAM VU6004909 shifts I/E balance toward inhibition.
(A) Schematic depicting whole-cell recording of SST-INs.
(B) Sample traces of current-clamp recordings from SST-INs in response to bath application of 3 μM DHPG in the presence of vehicle (black) or 10 μMVU6004909 (purple). Dashed lines represent baseline membrane potential. All experiments were conducted in the constant presence of the mGlu5 negative allosteric modulator MTEP (3 μM). Scale bars, 10 mV, 1 min.
(C) VU6004909 (10 μM) increases the SST-IN depolarization in response to 3 μM DHPG (two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test, p = 0.0067, n/N = 8/4 cells/mouse for Veh, 8/4 for VU′4909).
(D) A greater percentage of cells fire persistent action potentials in response to 3 μM DHPG in the presence of VU6004909. Number of cells responding/total cells recorded is denoted in each bar. Two-sided Fisher’s exact test, p = 0.026.
(E) Schematic depicting whole-cell recording of layer V pyramidal neurons.
(F) No difference in sEPSC frequency in layer V pyramidal neurons in response to bath application of 3 μM DHPG with and without 10 μM VU6004909 (two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test, p = 0.98, n/N = 9/4 for 3 μM DHPG, 9/4 for +VU′4909).
(G) VU6004909 (10 μM) potentiates the increase in sIPSC frequency in response to bath application of 3 μM DHPG (two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test, p = 0.023, n/N = 10/8 for 3 μM DHPG, 9/4 for +VU′4909).
(H) Ratio of sIPSC to sEPSC frequency (I/E ratio) in the same layer V pyramidal neuron during baseline and in the presence of 3 μM DHPG and 10 μM VU6004909. DHPG + VU6004909 significantly increased the I/E ratio (two-tailed paired t test, p = 0.012, n/N = 9/4).
(I) Sample traces of sIPSCs and sEPSCs in layer V pyramidal neurons during baseline and in the presence of 3 μM DHPG and 10 μM VU6004909. Scale bars, 20 pA, 250 ms. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
Data are represented as mean ± SEM. See also Figure S4.