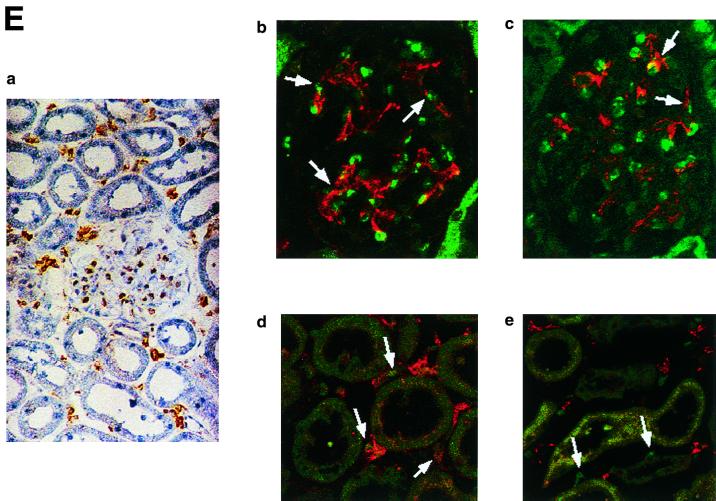
FIG. 6.
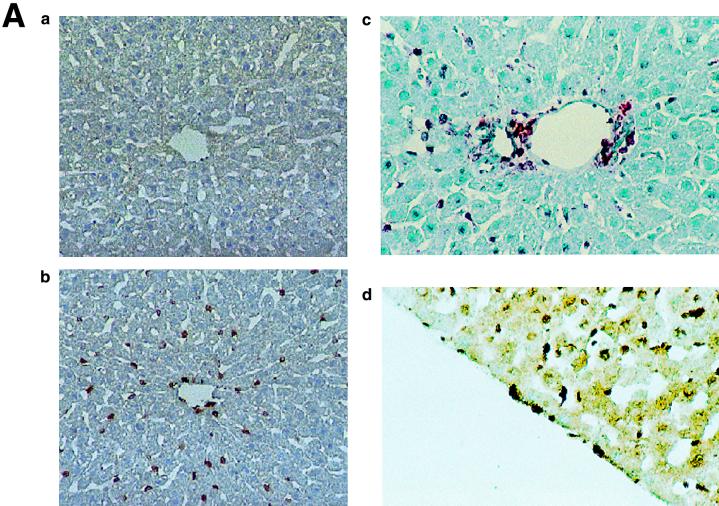
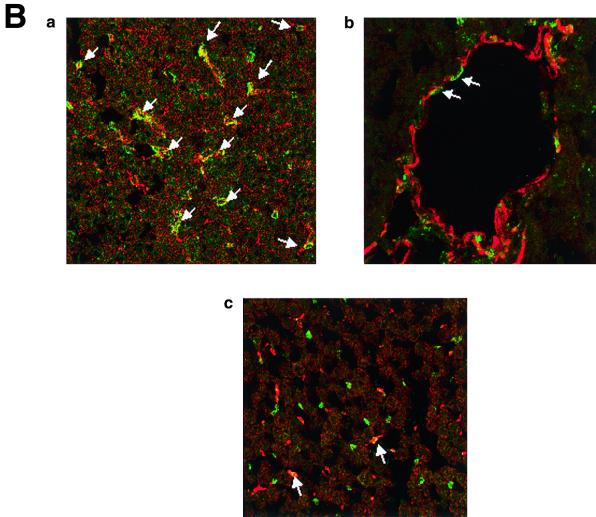
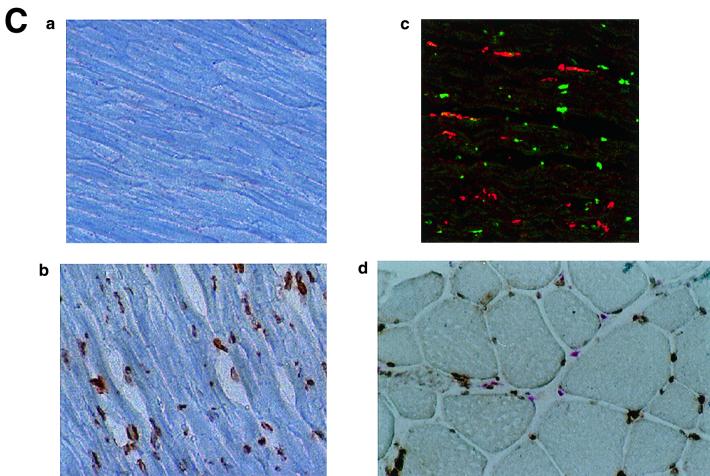
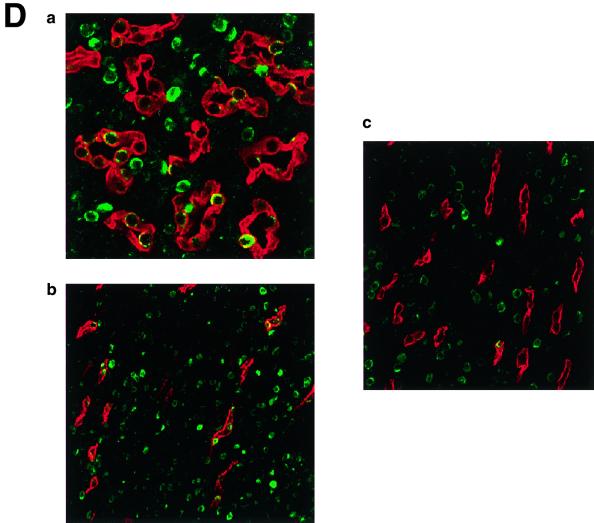
(A) KKLF in the liver. Cryostat sections of rat liver were incubated with preimmune serum (a) or anti-KKLF antibody (1:100) (b to d) in the TSA-Indirect system, and KKLF was visualized with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride (DAB) (b and d) or 3-amino-9-ethyl carbazole (c). The sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. Cells in siunusoids (b), portal fibroblasts (c), and subcapsular fibroblasts (d) were stained. (B) Double immunostaining of KKLF with desmin and ED-2 in the liver. (a) KKLF staining in sinusoids (green) was associated with desmin staining (red) and became yellowish (arrows). (b) The nuclei of desmin-positive (red) second-layer cells were also positive for KKLF (arrows). (c) ED-2 stainings identifying Kupffer cells (red) were only occasionally associated with KKLF staining (green). (C) KKLF staining in the heart and skeletal muscle. (a and b) Cryostat sections of rat heart were incubated with preimmune serum (a) or anti-KKLF antibody (1:100) (b) in the TSA-Indirect system, and KKLF was visualized with DAB (b). KKLF staining was observed in the interstitial cells (brown). (c) Double staining of KKLF (green) and ED-2 (red) in the heart. Most of the KKLF-positive cells were ED-2 negative. (d) KKLF staining in the skeletal muscle. KKLF visualized by DAB staining (brown) was observed in the interstitial cells between the muscle fibers and was not associated with the ED-2 staining (pinkish staining by Fast red). (D) Immunohistochemistry of rat KKLF in the inner medulla of the rat kidney. Double immunofluorescence of KKLF (green) and other marker proteins (red) in the inner medulla: AQP-2 (a) AQP-1 (b), or CLC-K1 (c) KKLF is colocalized with AQP-1 and AQP-2 but not with CLC-K1. Magnifications, ×400 (a) and ×200 (b and c). (E) KKLF in the glomeruli and cortex. (a) KKLF visualized with DAB was observed in the interstitial cells and cells in glomeruli in the cortex Magnification, ×200. (b) KKLF staining (green [arrows]) in the nuclei of glomeruli was mostly surrounded by desmin staining (red). (c) Only a small portion of KKLF staining (arrows) was associated with Von Willebrand factor staining (red). (d) Most of the KKLF staining in the interstitium was surrounded by ecto-5′-nucleotidase staining (arrows). (e) Most of the MHC-II-positive dendritic cells (red) did not have KKLF staining (green).