Fig. 9.
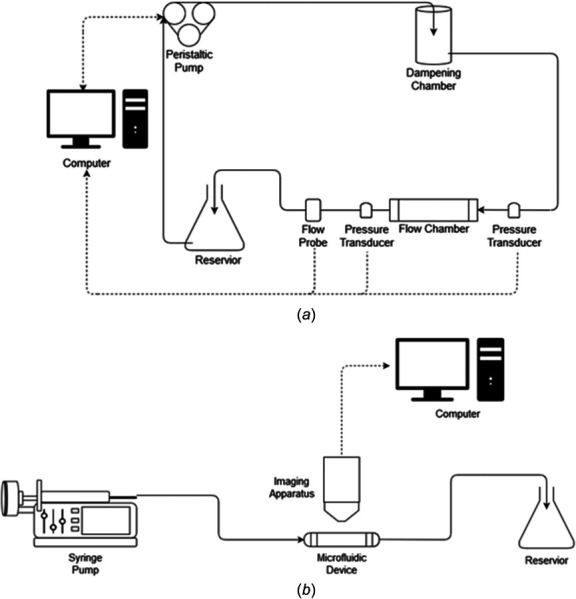
Process flow diagrams of fluid driving systems. (a) Process flow diagram for systems utilizing a peristaltic pump. Typically, fluid flow is driven from a reservoir by the pump. As the fluid exits the pump, it enters a dampening chamber, which minimizes pulsatile effects generated by the peristaltic pump. The fluid then flows through the flow chamber back to the reservoir, completing the flow system. Flow rate is monitored by a computer through a flow probe located downstream of the chamber. Pressure transducers can also be placed on either side of the flow chamber to monitor the pressure drop across the device. If changes are needed to the required flow rate, the computer will alter the angular velocity of the pump's rotor to produce the desired flow profile and shear stress for the study. (b) Process flow diagram of systems utilizing a syringe pump. Typically, a syringe loaded with fluid is mounted on a pump motor. The motor then pushes fluid from the syringe by a speed previously designated by the user. The fluid flows through the microfluidic device and into a discard reservoir. Real time imaging over the length of the study is collected by an imaging apparatus and is recorded by a computer.
