Fig. 1.
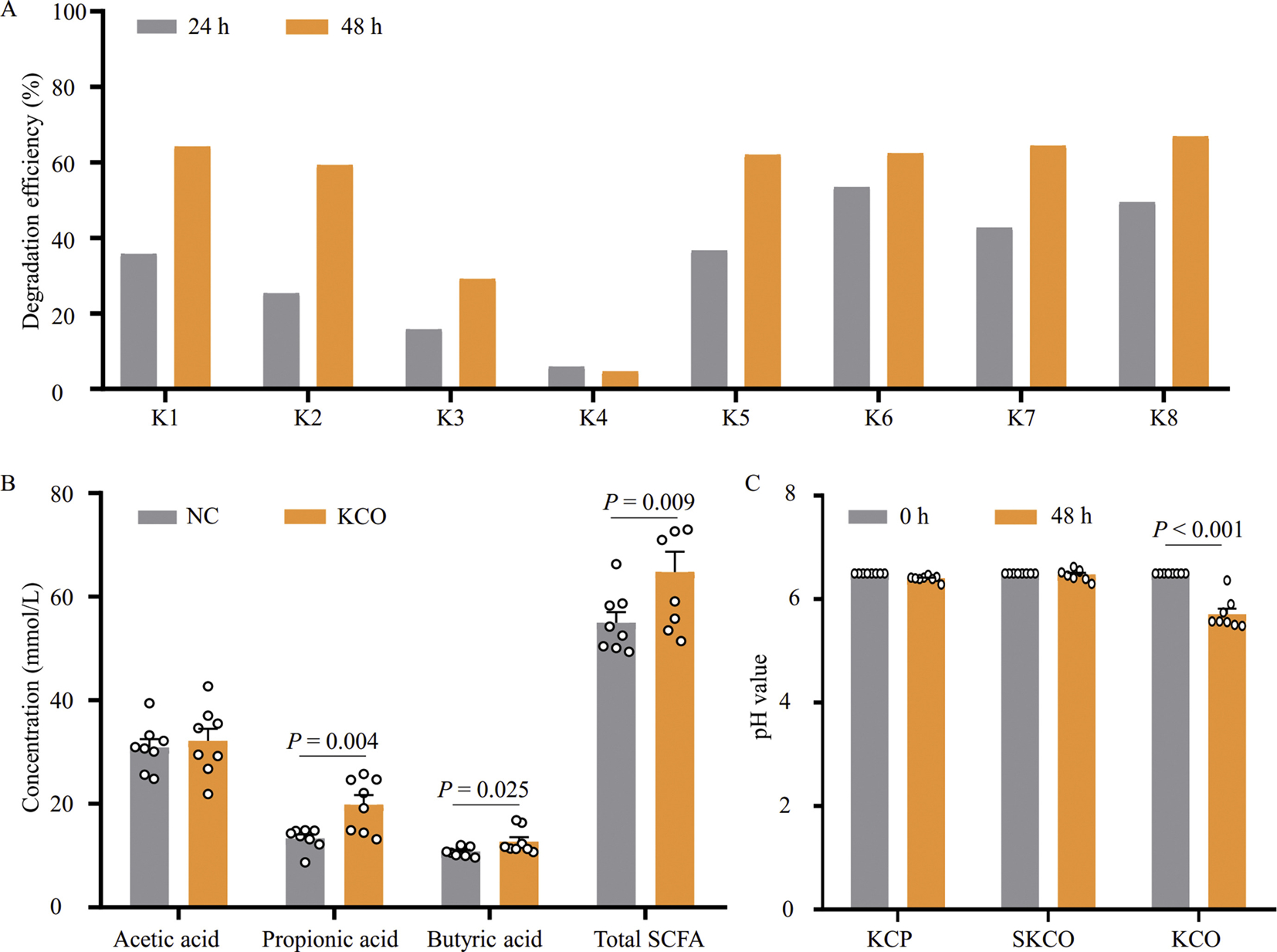
Degradation of KCO by human fecal microbiota. A: TLC measurements of KCO degradation efficiency. Degradation efficiency was calculated by quantifying changes in gray value of KCO spots in TLC using ImageJ software. Samples K1–K8 fecal microbiota were collected from healthy volunteers and subsequently inoculated into separate batch fermentations. B: HPLC detection of SCFAs produced during KCO degradation by fecal microbiota samples K1–K8 after 48 h of fermentation; total SCFAs include total contents of acetic, propionic, and butyric acids. No KCO was added to the NC. C: pH values before (0 h) and after (48 h) KCP, SKCO, or KCO fermentation. κ-carrageenan polysaccharides (KCP, 450 kDa), mild acid degraded κ-carrageenan (SKCO, 100 kDa), and κ-carrageenan oligosaccharides (KCO, 4.5 kDa); KCO, κ-carrageenan polysaccharides; TLC, thin-layer chromatography; SCFA, short chain fatty acid; NC, negative control.
