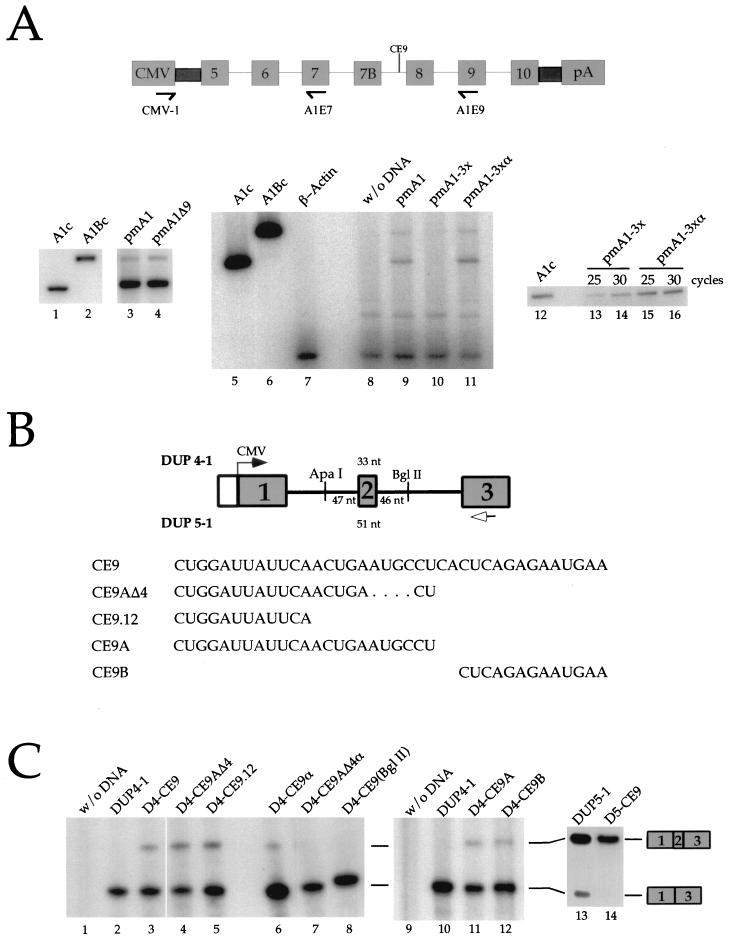
FIG. 4.
CE9 affects splicing in vivo. (A) CE9 prevents the production of fully spliced mRNAs. A genomic portion of the murine A1 gene was expressed in HeLa cells using the CMV-1 promoter. The relative position of CE9 is indicated, as well as the position of the oligonucleotides used for the RT-PCR assays performed on total RNA isolated 48 h posttransfection. A derivative carrying a deletion of CE9 was used (pmA1Δ9 [lane 4]). Three copies of CE9 or three copies of the complementary sequence of CE9 were inserted into pmA1Δ9 (pmA1-3x or pmA1-3xα, respectively). Reconstructed A1 or A1B cDNAs were used as controls in PCR assays (lanes 1, 2, 5, 6, and 12). RT-PCR amplification of the endogenous β-actin mRNA was performed independently on a mock transfection (lane 7) or simultaneously with the A1 minigene analysis with oligonucleotides CMV-1 and A1E9 (lanes 8 to 11). A separate RT-PCR assay was carried out with the CMV-1 and A1E7 oligonucleotides (lanes 12 to 16). The number of cycles used in the amplification rounds is indicated above the lanes. (B) Schematic representation of the DUP constructs and derivatives. The length of the central exon for DUP 4-1 and DUP 5-1 is indicated. The transcription start site is indicated by an arrow. The distance between the different cloning sites and the central exon is indicated. The arrow below exon 3 represents the oligonucleotide used for primer extension analysis. The RNA versions of the different oligonucleotides cloned into the DUP plasmids are shown at the bottom. (C) CE9 promotes the inclusion of artificial globin exon in vivo. DUP expression was analyzed by primer extension. Plasmid names are indicated above each lane. Each DUP 4-1, DUP 5-1, or derivative was generated by inserting oligonucleotides at the ApaI site, except for D4-CE9(BglII), for which BglII in the downstream intron was used (lane 8). Extension products were loaded onto a 5% acrylamide–8 M urea. The slightly abnormal migration of the 1-3 product in lane 8 is a gel artifact.