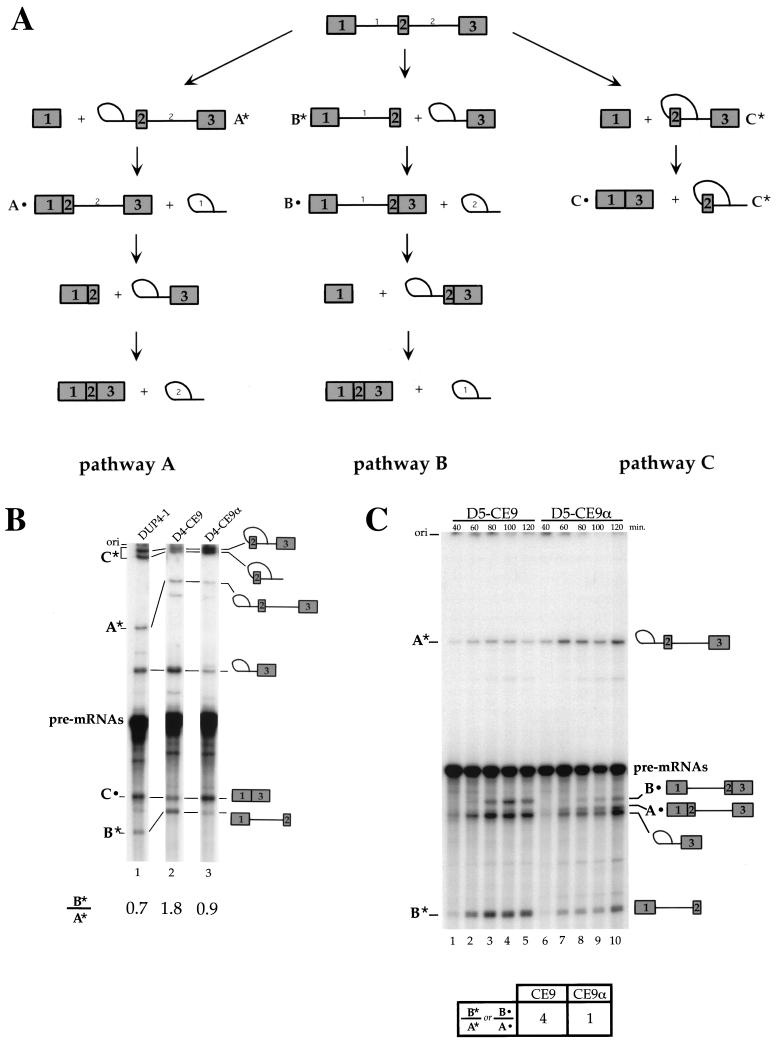
FIG. 5.
Effect of CE9 on DUP 4-1 and DUP 5-1 splicing in vitro. (A) Representation of different pathways used for the splicing of DUP pre-mRNAs. Pathway A occurs when intron 1 is the first intron to be removed, while pathway B takes place when intron 2 is spliced first. Pathway C corresponds to skipping of the internal exon. The splicing products, A*, A•, B*, B•, C*, and C•, indicate molecules that are unique to each pathway and correspond to the bands shown in the splicing gels (panels B and C). (B) CE9 shifts splicing in favor of pathway B. Labeled pre-mRNAs were incubated in HeLa extracts for 1 h. Splicing products were fractionated on an 11% acrylamide–8 M urea gel. Selected products are indicated. (C) CE9 also improves pathway B in DUP 5-1. Products specific to pathway A or B are indicated. Note that the band immediately below product A• corresponds to the intron 2-exon 3 lariat intermediate, a product common to pathways A and B. Pre-mRNAs were incubated under splicing conditions for the times indicated. Splicing products were loaded onto an 8% acrylamide–8 M urea gel. The ratio of product B* to product A* (or B•/A•) is indicated and is based on the 2-h time point. The structure of DUP pre-mRNA and derivatives is as shown in Fig. 4A, except that the labeled pre-mRNAs were synthesized in vitro using T7 RNA polymerase.