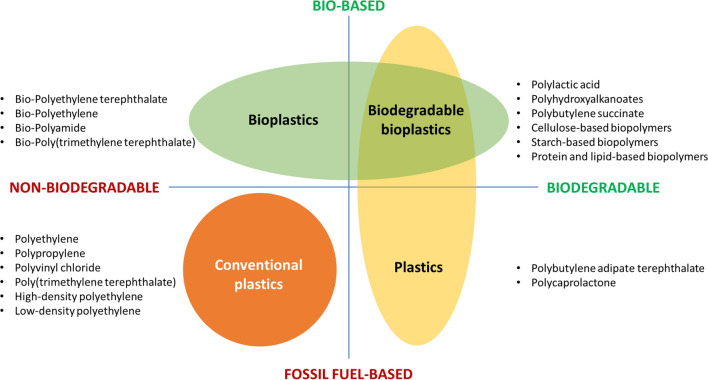
Fig. 6.
Biodegradability mapping for plant-based and fossil fuel-based plastic resins. Bioplastics such as polylactic acid, polyhydroxyalkanoates, polybutylene succinate as well as cellulose, starch, protein and lipids-based biopolymers can be decomposed by microorganisms to CO2, water and compost under controlled conditions. are not only bio-based but also biodegradable. Petrochemically derived polybutylene adipate terephthalate and polycaprolactone are also considered biodegradable. On the other hand, polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, poly(trimethylene terephthalate), high-density polypropylene and low-density polypropylene are petrochemically derived and non-biodegradable. Although polyethylene terephthalate, polypropylene, polyamide 11 and poly(trimethylene terephthalate) can be produced through bioresources, they cannot biodegrade naturally