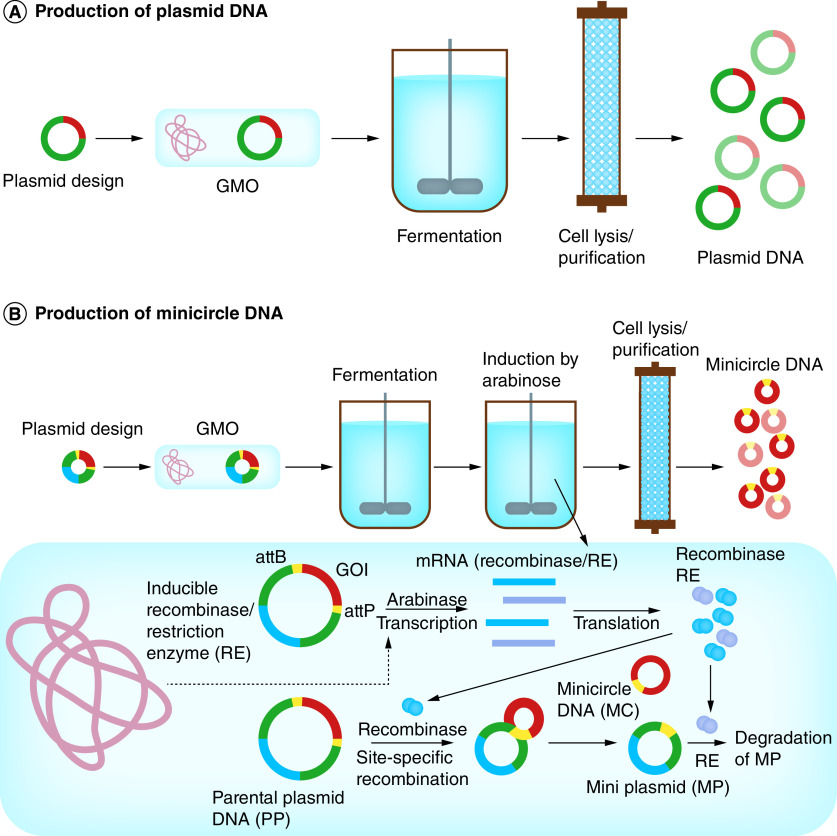
Figure 1. Production of circular DNA constructs.
(A) Production of plasmid DNA. The designed plasmid containing the GOI is transformed to the bacterial host to generate a GMO. After fermentation, bacterial cells are harvested and lysed through chemical, physical or mechanical methods. After the removal of solids from the lysate (clarification), several steps of purification such as chromatographic purification are used for the purification of plasmid DNA. (B) Production of minicircle DNA. After the growth of the genetically modified bacteria containing the parental plasmid, the expression of recombinase and the restriction enzyme is induced by arabinose from the plasmid or bacterial genome. The recombinase initiates the site-specific recombination between its recognition sequences (attB and attP), originating the minicircle DNA and a MP consisting of the bacterial backbone. Then, MP is degraded specifically by the RE. The minicircle DNA is extracted and purified after cell harvest, cell lysis, clarification and several steps of purification.
GOI: Gene of interest; GMO: Genetically modified organism; MP: Mini plasmid; RE: Recombinase.