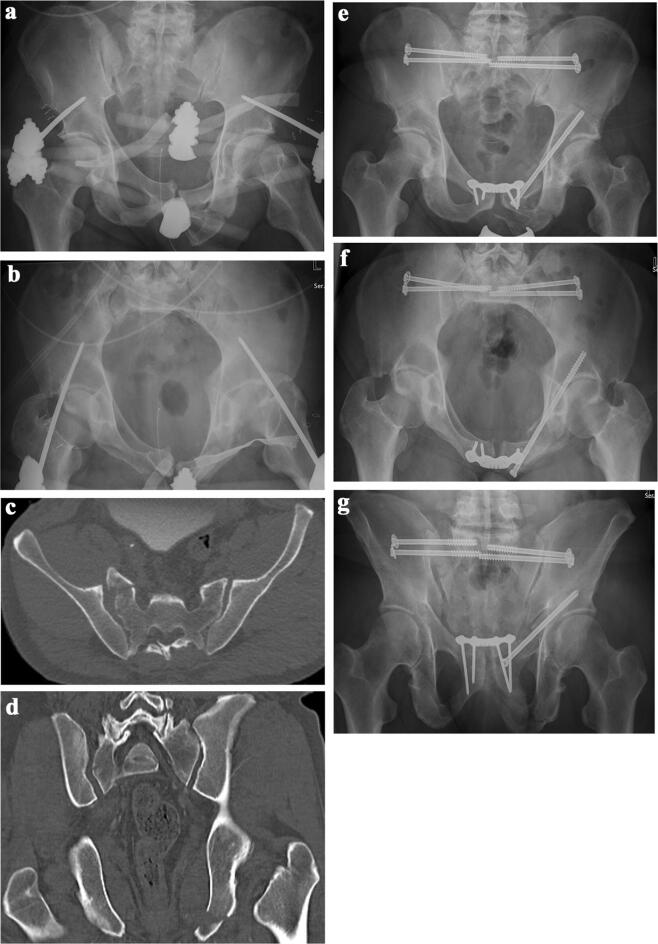
Fig. 2.
a 50-year-old male suffered an unstable pelvic ring injury due a traffic accident with high velocity. AP-view of the pelvis after application of an external fixator. A widening of the right iliosacral joint, a dislocation at the pubic symphysis and left-sided fractures of the superior and inferior pubic rami are visible. b Pelvic inlet view. A fracture at the anterior cortex of the right sacral ala and the displacement of the pubic symphysis are visible. c Axial CT-slice through the posterior pelvis. There is a widening of both iliosacral joints and a complete fracture through the right sacral ala. d Coronal CT reconstruction showing the widening of both iliosacral joints and left-sided fracture of the inferior pubic ramus fracture. e Postoperative AP-pelvic overview. Iliosacral joint disruptions and sacral fracture were stabilized with two iliosacral screws on both sides. Dislocation of the pubic symphysis was reduced and stabilized with plate and screw osteosynthesis. Left-sided superior pubic ramus fracture was reduced with a retrograde transpubic screw. There were no postoperative problems. No postoperative CT scan was made. f Pelvic inlet view. g Pelvic outlet view