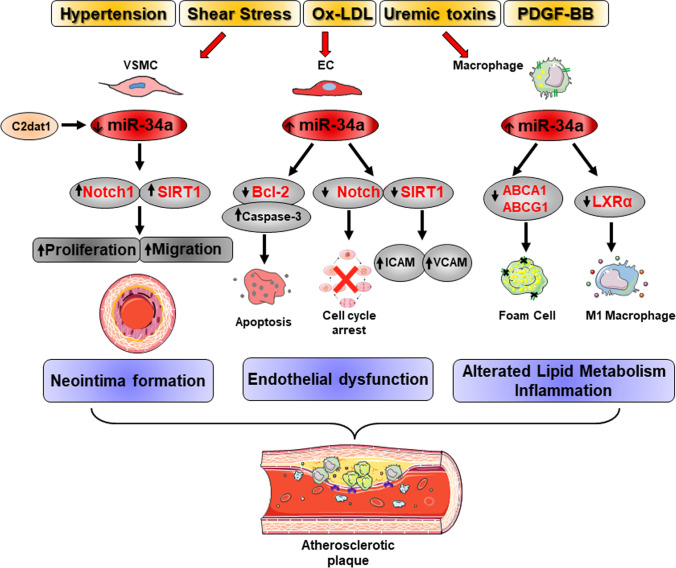
Fig. 5.
miR-34a in atherosclerosis. Atherogenic stimuli differentially modulate miR-34a expression in vascular cells. miR-34a downregulation due to Platelet-derived Growth Factor B (PDGF-BB), oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) and uremic toxins induces the sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) and Notch1 upregulation that stimulate vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) proliferation and migration and ultimately neointima formation. The long non-coding RNA CAMK2D‐associated transcript 1 (C2dat1) suppresses miR-34a expression in VSMCs. Atheroprone oscillatory shear stress causes miR-34a upregulation and endothelial cells (ECs) activation in terms of increased expression of Vascular Cell Adhesion Protein 1 (VCAM1) and Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 (ICAM1) by SIRT1. Similarly, ox-LDL and uremic toxins stimulate miR-34a synthesis and ECs apoptosis and inhibition of their proliferation through B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and Notch1 downregulation, respectively. In macrophages, ox-LDL increases miR-34a levels that target the cholesterol transporters ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 1 (ABCA1) and ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 1 (ABCG1) and subsequently reduces macrophages cholesterol efflux capacity and their differentiation in foam cells. Moreover, miR-34a enhances the secretion of inflammatory cytokines by directing M1-type macrophage differentiation through the nuclear hormone Liver X receptor α (LXRα). Altogether, these events alter lipid metabolism and promote inflammation facilitating atherosclerotic plaque formation. In red are highlighted known direct targets of miR-34a