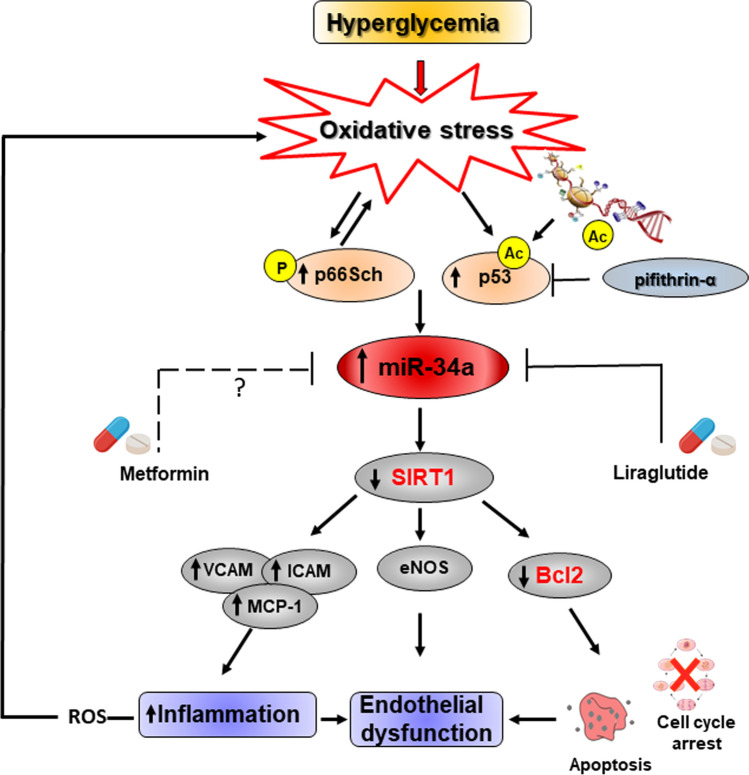
Fig. 6.
Molecular pathways triggered in vascular cells by miR-34a in diabetes. Hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress promotes the acetylation of p53 transcription factor as well as p66Shc phosphorylation that are responsible for miR-34a upregulation and consequent reduced sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression in endothelial cells (ECs). SIRT1 downregulation, likely through NF-kB acetylation/stabilization, promotes Vascular Cell Adhesion Protein 1 (VCAM1), Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 (ICAM1) and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) protein expression leading to inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. This deleterious network contributes to intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and cellular damage exacerbation. The p53-specific chemical inhibitor pifithrin‐α mitigates high glucose‐induced miR‐34a expression and SIRT1 downregulation. Glucose lowering agents, such as Metformin and Liraglutide, exert anti-aging, anti-inflammatory and vascular protective effects by miR-34a expression regulation