Figure 2:
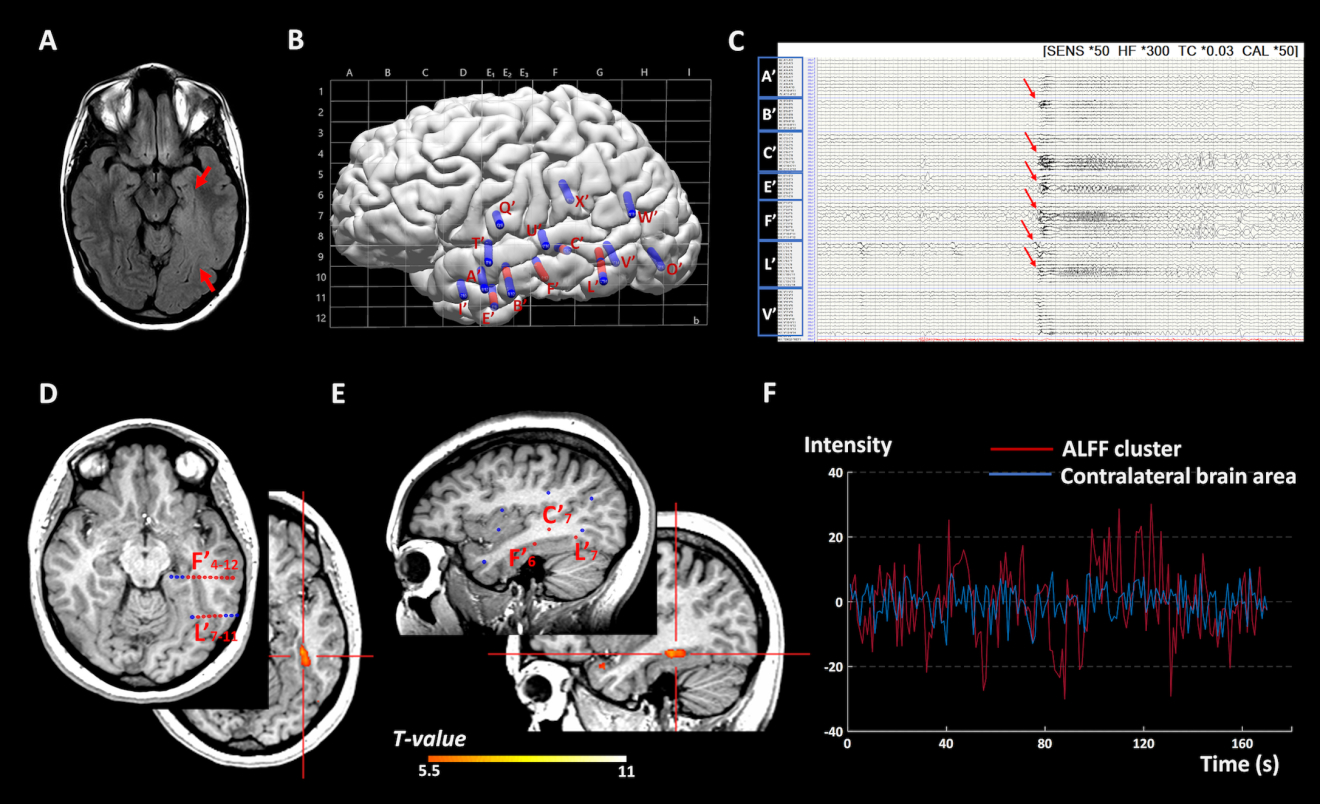
Representative case 1: Illustration of a concordant ALFF cluster with the SEEG-defined SOZ in a patient with a widespread dysplastic MRI lesion of unclear boundary at the left basomedial temporo-occipital area (P1 in table 1). SEEG was performed to help delineate the extent of the SOZ, especially the involvement of the ipsilateral hippocampus anteriorly, speech area dorsally and visual area posteriorly. A) 3T 2D FLAIR image showing abnormal hyperintensity signal extending from the left hippocampus to the occipital lobe (red arrows). B) SEEG implantation map shown with Talairach grid superimposed, including 14 electrodes and 160 contacts (contacts indicating SOZ marked with red, other contacts marked with blue). C) Bipolar montage of relevant SEEG channels (20-second epoch): Typical seizure showed onset involving primarily contacts L’1–5 (lesion), L’7–11 and F’4–12 (basal temporal region) along with E’4–7, B’3–6 (anterior temporal region) and C’7–11 (superior temporal sulcus) characterized by paroxysmal low amplitude fast activity (red arrows). D) axial view and E) sagittal view: The ALFF activation cluster, indicated by the red crossbar, was located inside the SOZ noted by the red SEEG contacts. F) time series plots of the BOLD signal fluctuation versus time in seconds. Time series were extracted from the peak of the SOZ-concordant ALFF activation cluster in the left fusiform gyrus (red line) showed significantly higher amplitude than that of the corresponding contralateral brain area (blue line), which suggests increase of regional neural activities within the SOZ. This patient has been seizure-free for 1.75 years following left temporal lobectomy.
ALFF= amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations; s= second; SOZ= seizure onset zone; SEEG= Stereo-electroencephalography; MRI= magnetic resonance imaging; BOLD= Blood oxygenation level dependent.
