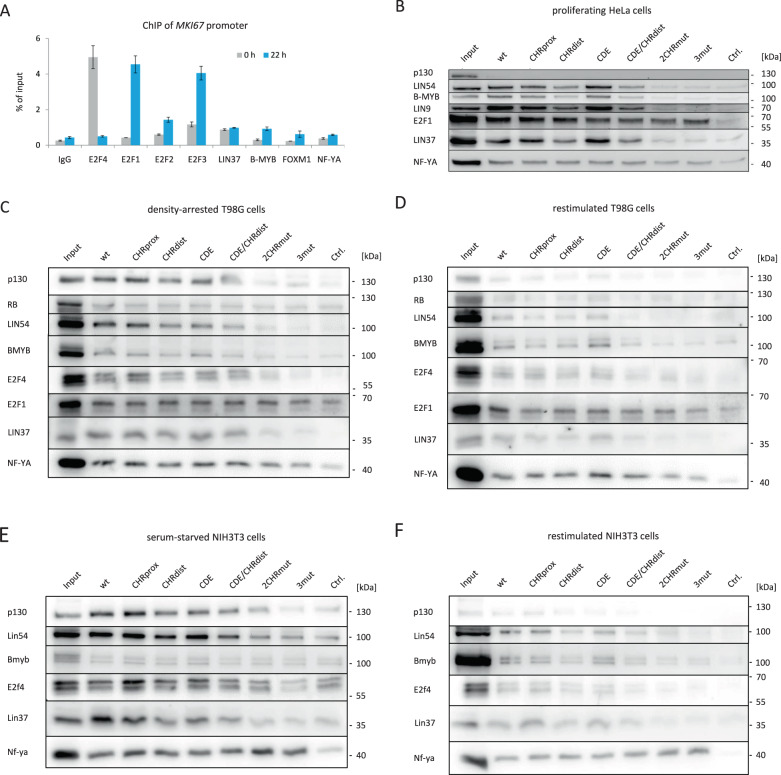
Fig. 4. DREAM, E2F, and FOXM1/B-MYB/MuvB complex components bind to the MKI67 promoter in vivo and in vitro.
E2F4 and p130 were detected as representatives of DREAM. B-MYB is specific for B-MYB-MuvB. NF-YA is a subunit of NF-Y. E2F1/2/3 proteins are detected to represent E2F proteins independent of DREAM. FOXM1 detection indicates FOXM1-MuvB binding. LIN37 and LIN54 are representative components of all MuvB-based complexes. A In vivo protein binding to the MKI67 promoter in serum-starved (0 h, gray) and restimulated (22 h, blue) human T98G cells was analyzed via chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) followed by real-time qPCR. Mean values ± SD are given of one representative experiment with two technical replicates for each precipitate. B–F Nuclear extracts from proliferating HeLa cells (B), density-arrested human T98G cells (C), restimulated T98G cells (D), serum-starved mouse NIH3T3 cells (E), as well as restimulated NIH3T3 cells (F) were subjected to DNA affinity purification, to assay in vitro binding of complex components by western blot analysis. Fragments of the MKI67 promoter containing wild-type (wt) or mutant promoter fragments with mutations in CHRprox, CHRdist, and CDE sites were used for DNA probes. 2CHRmut, CDE/CHRdist, and 3mut mutant probes carry combined mutations in CHRdist/CHRprox, CDE/CHRdist, and CHRdist/CHRprox/CDE, respectively. As a negative control of background binding (Ctrl.), a fragment of the mouse Gapdh2 promoter was employed. Input samples were taken from the nuclear extract before purification. For detection with one specific antibody, all samples were run on the same gel and analyzed via western blotting.