Fig. 1. M. shengliensis AmaM and ZC-1 corrinoid protein and methyltransferase phylogeny.
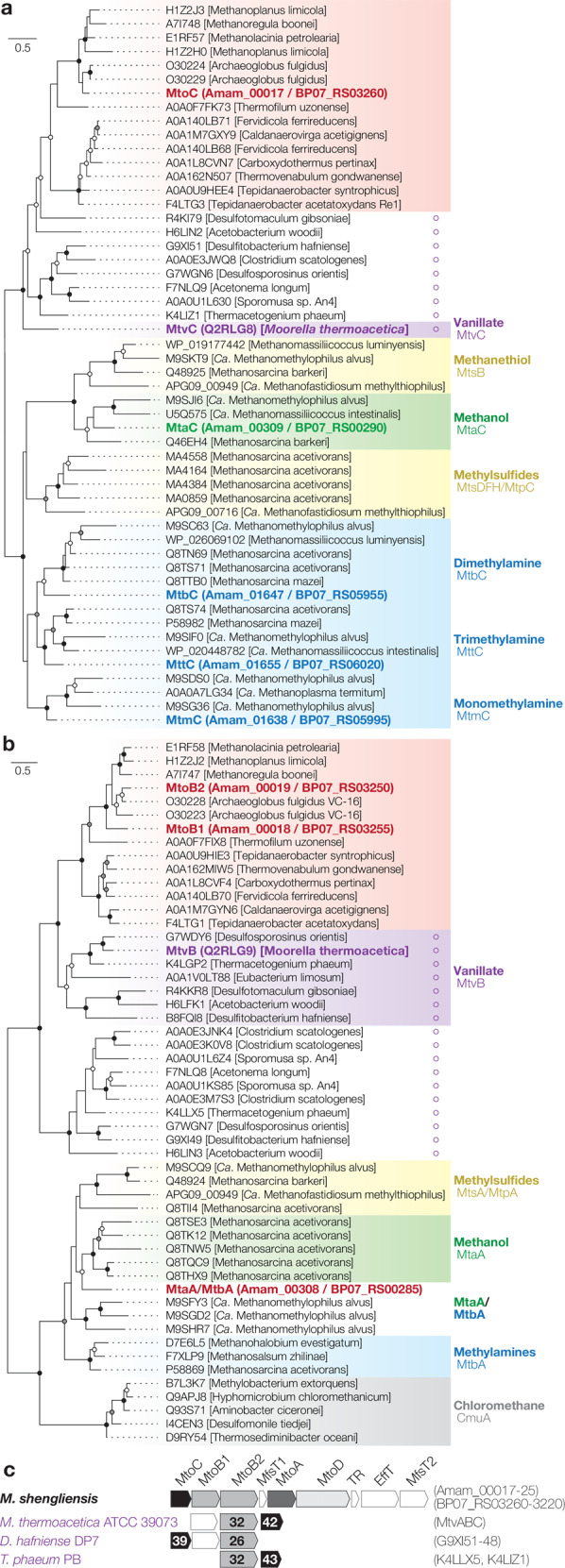
a A phylogenetic tree of AmaM methyltransferase corrinoid proteins (red and bolded) and homologs were generated through sequenced alignment via MAFFT v7.394 and tree calculation via RAxML-NG v0.5.1b. The homologs include those specific to vanillate (MtvC; purple), MeOH (e.g., MtaC; green), methylated thiols (e.g., MtsB; yellow), and methylamines (e.g., MtmC; blue). For methyltransferase corrinoid proteins fused with their partner methyltransferase, only the cobalamin-binding region was extracted for this alignment. In addition, a novel cluster of bacterial methyltransferases is shown, including those from ArOCH3-metabolizing anaerobes (indicated with purple circles). Bootstrap values are shown for 200 iterations (>90% black, >70% gray, >50% white). b Phylogenetic tree of MtaA/CmuA family (TIGR01463, cd03307, and IPR006360) and MtvB-related methyltransferases, including those from M. shengliensis (red and bolded) and M. thermoacetica (purple and bolded). MT2 for MeOH (e.g., MtaA; green), methylamine (e.g., MtbA; blue), and MeOH/methylamine bifunctionally; bifunctional MT1/MT2 for methylated thiols (e.g., MtsA; yellow); and MT1 for chloromethane (gray) are shown. Methyltransferases affiliated with ArOCH3-metabolizing anaerobes (purple circles) form a novel cluster. c The operon encoding the novel corrinoid protein (MtoC) with methyltransferases (MtoB1, MtoB2, and MtoA) and corrinoid protein activase (MtoD) along with potential aromatic compound transporters (MfsT MFS transporter, EffT Efflux transporter) and a transcriptional regulator (TR). Operons identified in bacterial ArOCH3 metabolizers are also shown with amino acid sequence percent identity with MtoC and MtoB2.
