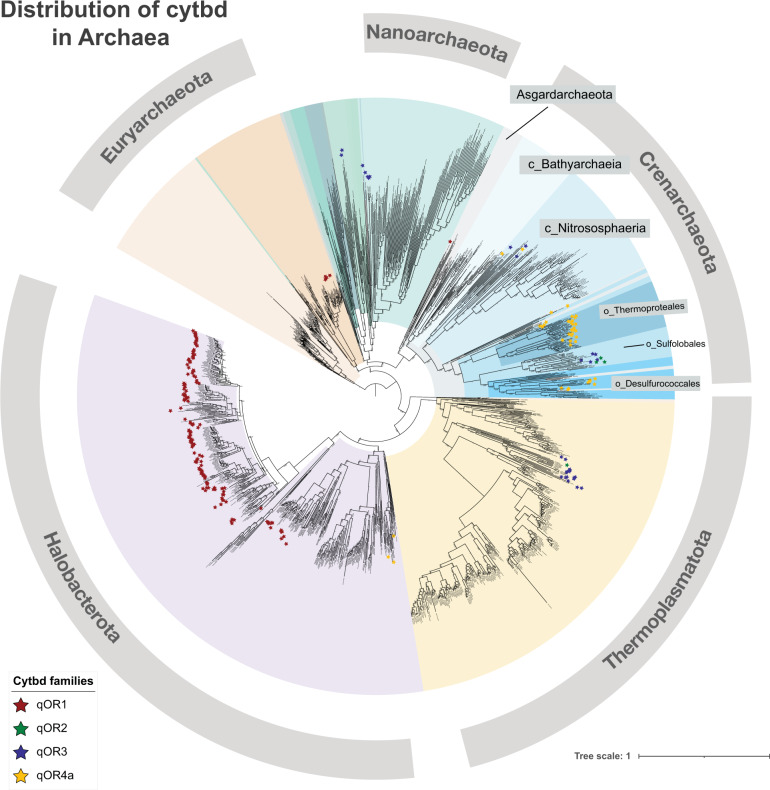
Fig. 3. Distribution of cytochrome bd-type oxygen reductases in Archaea.
Concatenated gene alignments were made from the archaeal genomes in GTDB using Anvi’o. A phylogenetic tree was made from the concatenated gene alignments using FastTree. All CydA sequences were extracted from GTDB genomes using BLAST with an e-value of 1e−1. The sequences were then filtered to remove CydA sequences without characteristics of the quinol binding site and then classified using a Hidden Markov Model (HMM)-based classifier trained to identify the families—qOR1, qOR2, qOR3 and qOR4a. CydA sequences from each family were then mapped back to each species, and visualized along with the species tree on the iTOL server. Most phyla of the domain Archaea were distinguished by color and a few classes of the phylum Crenarchaeota were labelled to emphasize the presence of CydAA’. It is clear that CydAA’ is almost exclusive to the order Thermoproteales and Desulfurococcales.