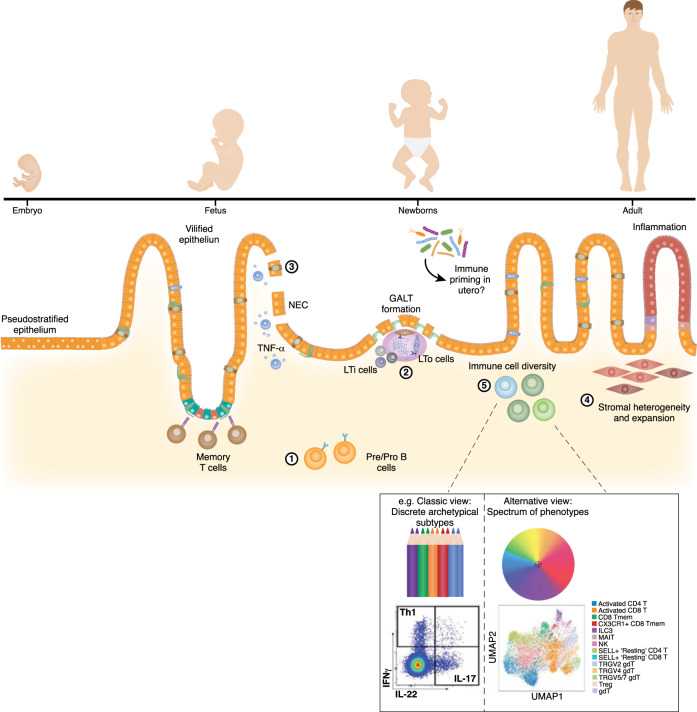
Fig. 2. ScRNAseq advances in understanding mucosal immunity throughout life and during disease.
(1) Building from observations of lymphocyte maturation in the prenatal intestines, single-cell studies have promoted the concept that T and B cell activation up to second-trimester development is in support of intestinal development rather than in response to microbial seeding21,74–76. (2) Key players in gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) formation previously identified in developing mouse gut have been identified in scRNAseq studies of human fetal gut, with additional cell heterogeneity identified21,24. (3) TNF-α-producing CD4+ T cells resolved at single-cell level are enriched in the preterm intestines, likely contributing to epithelial damage observed in necrotising enterocolitis (NEC)77. (4) Intestinal stromal heterogeneity has been determined, and expanded subtypes in inflammatory bowel disease linked with pathology16–18. (5) Inlaid box depicts the classical idea of discrete immune cell subsets versus a spectrum of phenotypes determined through scRNAseq analyses88. LTi lymphoid tissue inducer, LTo lymphoid tissue organiser.