FIG 2.
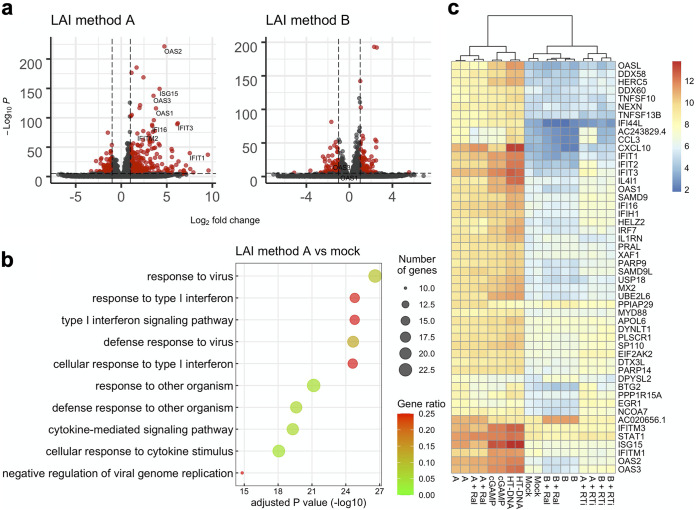
A gene expression signature of type I IFN signaling depends on plasmid purification protocols and viral DNA synthesis. THP-1 cells were either infected with HIV-1 under different conditions or treated with cGAS stimulatory molecules (cGAMP and HT-DNA). Total RNA used for construction of RNA-sequencing libraries was extracted from cells harvested at 16 h after infection, except for those treated with cGAMP or HT-DNA, which were harvested at 2 h after treatment. (a) Volcano plots depict gene expression differences as fold differences (log2 transformed) between mock-infected cells and virus-infected cells. A representative set of ISGs is labeled. Horizontal dashed lines correspond to an arbitrary cutoff P value of 10−6. Vertical lines correspond to a log2 fold change of ± 2. Genes that satisfy these cutoff values are shown in red, while those that do not are shown in black. (b) Shown are the top 10 Gene Ontology (GO) terms enriched in the sample prepared from THP-1 cells infected with the WT virus prepared using method A. All these terms belong to a GO aspect called “biological process.” Genes with a log2 fold change of greater than 2 were ranked based on adjusted P values before the top 50 upregulated genes were selected and subjected to GO analysis. Dot sizes indicate the number of genes associated with a corresponding GO term, whereas dot colors indicate the proportion of enriched genes in all the genes that belong to a given GO term. (c) The heat map depicts gene expression levels across different samples and was generated using normalized read counts. The top 50 upregulated genes in the sample “A” (i.e., LAI virus prepared with method A) compared to the mock-infected samples are shown. These upregulated genes were selected with the following criteria: adjusted P values of <0.01, log2 fold change of >2. Ral, raltegravir; RTi, reverse transcription inhibitors (100 μM lamivudine [3TC], 200 μM AZT, 50 μM nevirapine).