Figure 1. Differential regulation of tonic inhibition by GluN2 subunits.
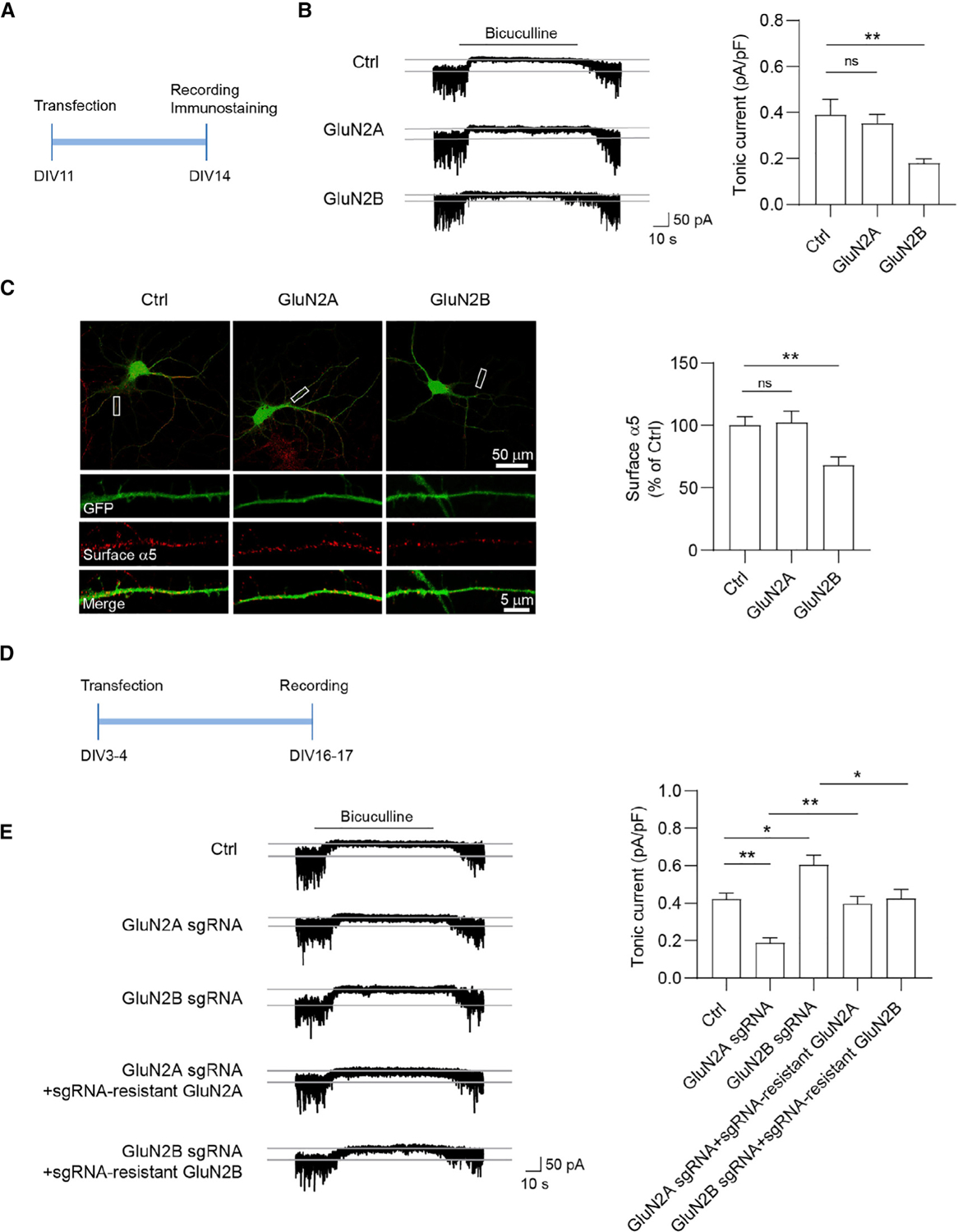
(A) Overexpression experiment design. Neurons were transfected at 11 days in vitro (DIV11) for 72 h and then recorded for tonic inhibitory currents at DIV14.
(B) GluN2B, but not GluN2A, overexpression decreased tonic currents in cultured neurons. n = 10–13 for each group, one-way ANOVA test, F(2,31) = 5.029, p = 0.0128 with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Ctrl versus GluN2B: p = 0.0093.
(C) GluN2B, but not GluN2A, overexpression decreased surface α5 expression in cultured neurons. n = 28–31 for each group, one-way ANOVA test, F(2,87) = 6.369, p = 0.0026 with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, Ctrl versus GluN2B: p = 0.0071.
(D) Knockout (KO) experiment design. Neurons were transfected at DIV3–DIV4 and then recorded for tonic currents at DIV16–DIV17.
(E) GluN2A KO decreased tonic currents, whereas GluN2B KO increased tonic currents. The changes in tonic currents induced by either GluN2A or GluN2B KO were restored back to the control level by co-expression of corresponding sgRNA-resistant constructs, respectively. n = 8–10 for each group, one-way ANOVA, F(4,39) = 13.12, p < 0.0001 with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, Ctrl versus GluN2A sgRNA: p = 0.0039; Ctrl versus GluN2B sgRNA: p = 0.0224: GluN2A sgRNA versus GluN2A sgRNA + sgRNA-resistant GluN2A: p = 0.0091; GluN2B sgRNA versus GluN2B sgRNA + sgRNA-resistant GluN2B: p = 0.0202.
*p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.
See also Figure S1.
