Figure 3. GluN2A-NMDARs are required for homeostatic potentiation of tonic inhibition.
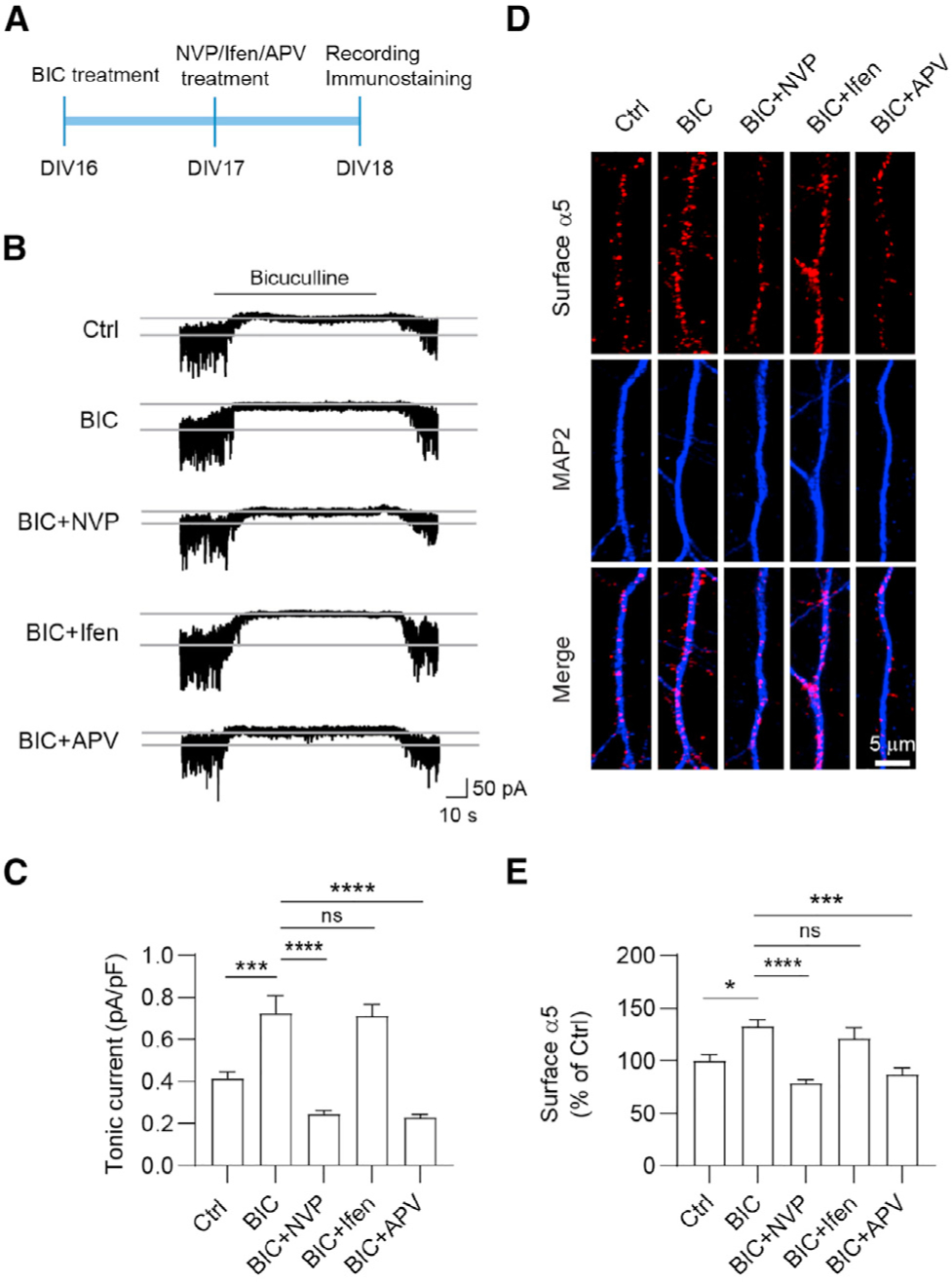
(A) Experimental design. Hippocampal neurons at DIV16 were treated with bicuculline (BIC, 40 μM), and at DIV17 they were treated with NVP (100 nM), Ifen (5 μM), or APV (100 μM) for 24 h before recording.
(B and C) NVP and APV treatment abolished BIC-induced potentiation of tonic currents. n = 10 for each group, one-way ANOVA test, F(4,45) = 25.32, p < 0.0001 with Tukey’s multiple comparison test, Ctrl versus BIC: p = 0.0004; BIC versus BIC+NVP: p < 0.0001; BIC versus BIC+APV: p < 0.0001.
(D and E) NVP and APV treatment abolished BIC-induced potentiation of surface α5 expression. n = 20–26 for each group, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, Ctrl versus BIC: p = 0.0189; BIC versus BIC+NVP: p < 0.0001; BIC versus BIC+APV: p = 0.0002.
*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.
