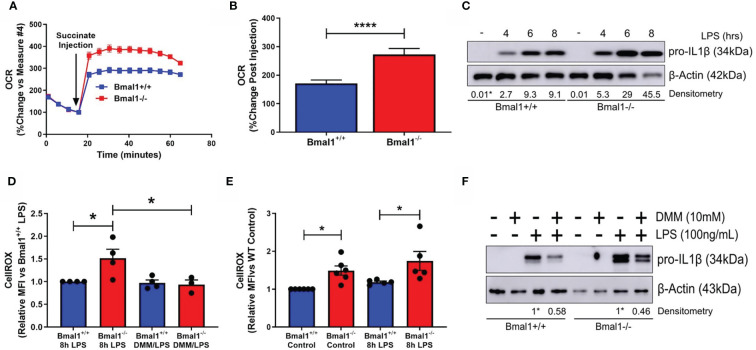
Figure 2.
SDH-derived ROS are driving increased inflammation in macrophages with deletion of Bmal1. Bmal1+/+ and Bmal1-/- BMDMs were incubated in an isosmotic, ADP-supplemented mitochondrial assay solution and permeabilized with digitonin. (A) Seahorse XF analysis was used to analyse the change in OCR in response to injection of succinate (1.25 mM). (B) Response to succinate was measured in terms of %change in OCR directly following injection of succinate. Assay results are presented +/- SEM and are representative of n=3 independent experiments. BMDMs were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) and (C) stained with CellROX to measure levels of reactive oxygen species by flow cytometry or (D) lysed for analysis of pro IL-1β protein expression by Western blot using β-Actin as a loading control. (E) Reactive oxygen species and (F) pro IL-1β protein expression were measured following pretreatment with DMM before stimulation with LPS. Western immunoblot data presented is representative of n=3 independent experiments. Pro IL-1β time course densitometry is relative to the Bmal1+/+ control band. Densitometry for Bmal1+/+ and Bmal1-/DMM/LPS bands is relative to their LPS bands. These bands are indicated by * symbols. Flow cytometry data presented is at least n=3 independent experiments +/- SEM with each data point representative of at least 5,000 events from one sample. Statistical analysis was performed for Seahorse XF data by unpaired student’s t test and for flow cytometry data by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (*p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001).