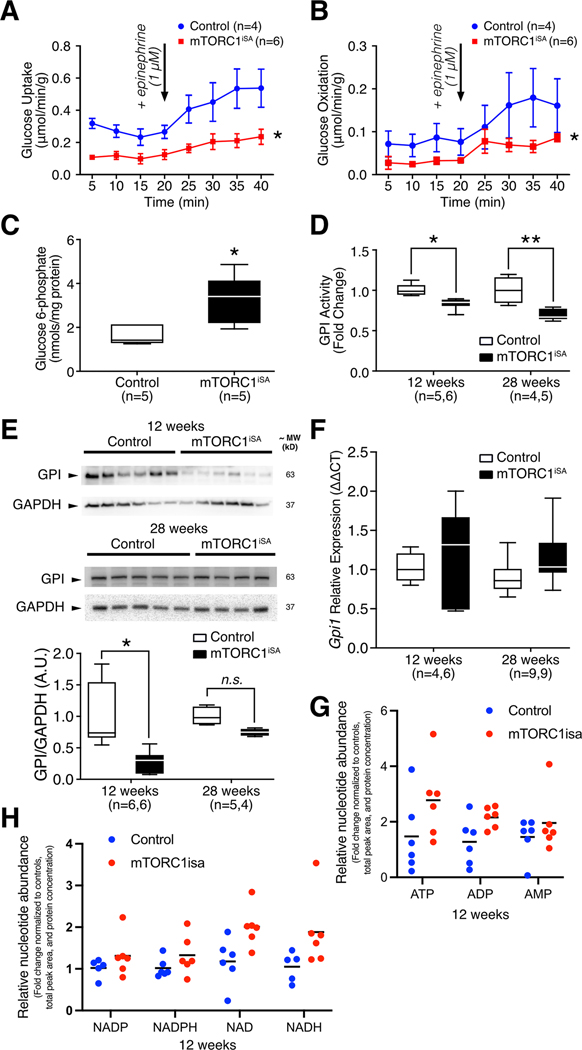
Figure 3. Sustained mTORC1 activation in adult mouse hearts induces metabolic remodeling in mTORC1iSA mice at 12 weeks.
(A) Rates of glucose uptake and (B) glucose oxidation were decreased in retrogradely perfused mTORC1iSA mouse hearts at 12 weeks (n= 4 Control and 6 mTORC1iSA mice). (C) G6P metabolite levels were elevated in the heart muscle of mTORC1iSA mice at 12 weeks (n=5 mice per group). (D) GPI activity is depressed at 12 weeks (n= 5 Control and 6 mTORC1iSA mice) in mTORC1iSA and this decrease is sustained through 28 weeks (n= 4 Control and 6 mTORC1iSA mice). (E) GPI protein levels measured in mTORC1iSA mouse hearts at 12 weeks (n=6 mice per group) were decreased and this decrease is attenuated at 28 weeks (n= 5 Control and 4 mTORC1iSA mice). (F) There was no change in the transcription of GPI at either 12 weeks (n= 4 Control and 6 mTORC1iSA mice) or 28 weeks (n=9 mice per group). (G and H) Levels of ATP, ADP, and AMP, as well as Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotides were similar in mTORC1iSA than in control mouse hearts at 12 weeks (n=6 mice per group). Nucleotide abundance is expressed as fold-change from control, and was normalized by total peak area and protein concentration. Statistical significance was calculated using two-way ANOVA (A and B), unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test (C), two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test (D and F), unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test with correction for multiple comparisons using a FDR of 0.1 (G-H); *p<0.05, **p<0.01.