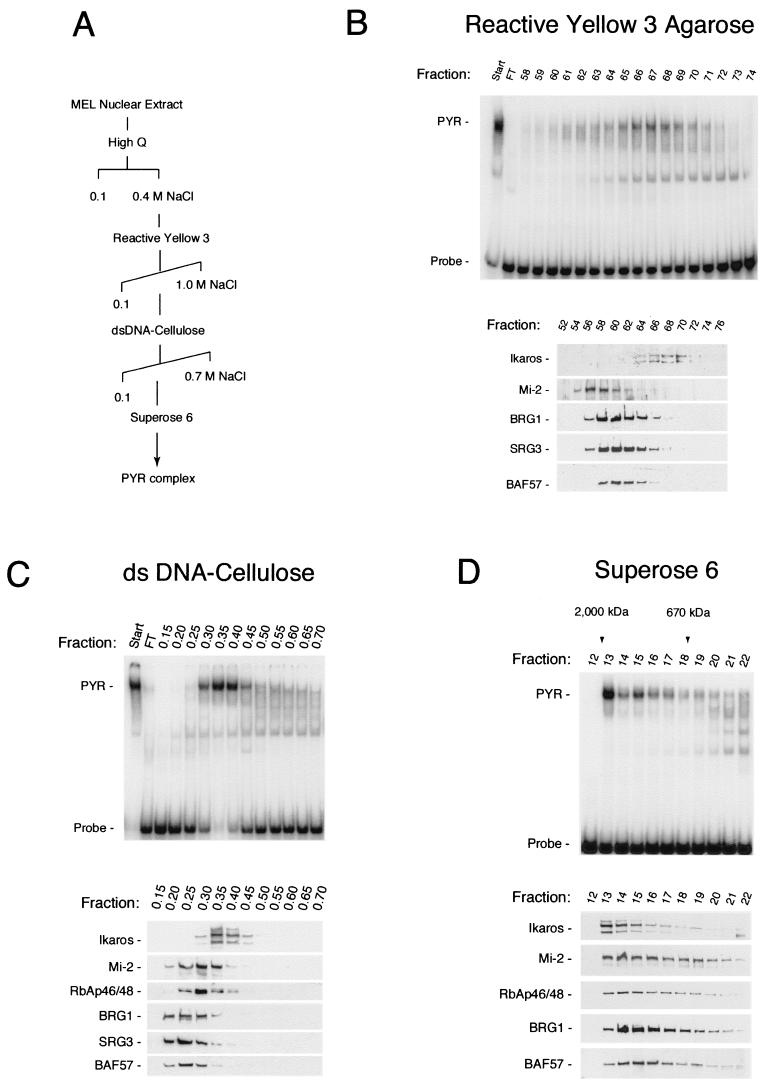
FIG. 4.
PYR complex DNA-binding activity cofractionates from MEL nuclear extract with Ikaros and a subpopulation of SWI/SNF and NuRD protein. (A) Purification scheme. The PYR complex was purified from MEL nuclear extract in four chromatographic steps using High Q Macroprep (Bio-Rad; 0.1 to 0.4 M NaCl step elution), reactive yellow 3-agarose (Sigma; 0.1 to 1.0 M NaCl gradient), double-stranded (ds) DNA-cellulose (calf thymus DNA-cellulose [Sigma], 0.1 to 0.7 M NaCl step gradient), and Superose 6 (Amersham Pharmacia) columns. (B) Chromatography on reactive yellow 3-agarose shows peak PYR complex DNA-binding activity by gel shift assay (PYR) eluting in fractions 64 through 70 (upper panel), corresponding precisely with the elution pattern of Ikaros by Western blotting (lower panel). The majority of NuRD (Mi-2) and SWI/SNF (BRG1, SRG3, and BAF57) proteins elute prior to fraction 64, with some overlap into fractions 64 through 68. Fractions 65 through 70 were pooled, concentrated, adjusted to 0.1 M NaCl, and loaded onto the DNA-cellulose column (C). Peak PYR complex DNA-binding activity elutes off the DNA cellulose column in fractions 0.3 through 0.45 (upper panel), again corresponding precisely with the elution pattern of Ikaros (lower panel). Much of the NuRD (Mi-2 and RbAp46/48) and SWI/SNF (BRG1, SRG3, and BAF57) proteins elutes prior to fraction 0.3, but there is greater overlap into the PYR DNA-binding fractions than seen with reactive yellow 3-agarose. Fractions 0.3 through 0.45 were pooled, concentrated, and loaded onto the Superose 6 gel filtration column (D). Again, PYR complex DNA-binding activity, which elutes in high-molecular-mass fractions (1 to 2 MDa, upper panel), corresponds exactly with the elution pattern of Ikaros by Western blotting (lower panel). Here, however, both NuRD (Mi-2 and RbAp46/48) and SWI/SNF (BRG1 and BAF57) subunits cofractionate very closely with PYR DNA-binding activity and Ikaros. FT, failure to bind.