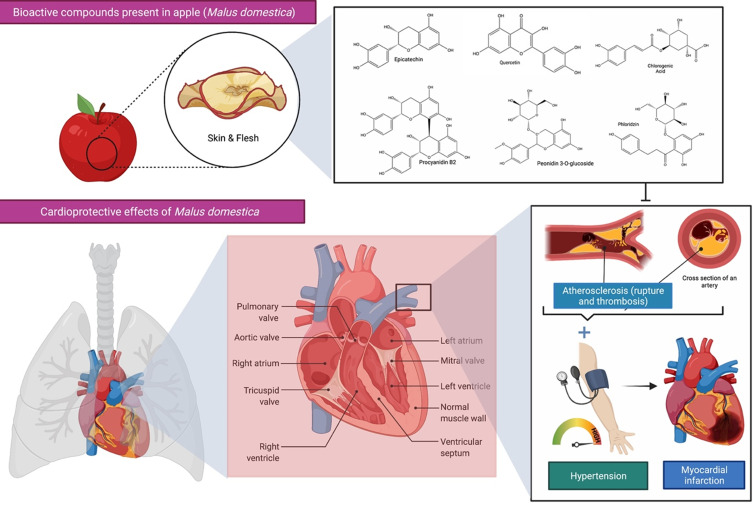
Figure 3.
Bioactive compounds present in apple (Malus domestica) and its cardioprotective effects. Apple polyphenols are abundant in the flesh and peel of the fruit and contribute to the improvement of blood pressure, endothelial function, and arterial stiffness in those at increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVDs). A healthy heart permits blood to be pumped out via a network of blood channels known as arteries. The left side of the heart takes oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it out via a big artery called the aorta, while deoxygenated blood returns to the heart via blood vessels called veins. However, atherosclerosis, a buildup of plaque inside the arterial walls, may cause the arteries to narrow, making blood circulation more difficult. The combination of hypertension and atherosclerosis will eventually result in more significant issues such as myocardial infection, more often referred to as a heart attack.