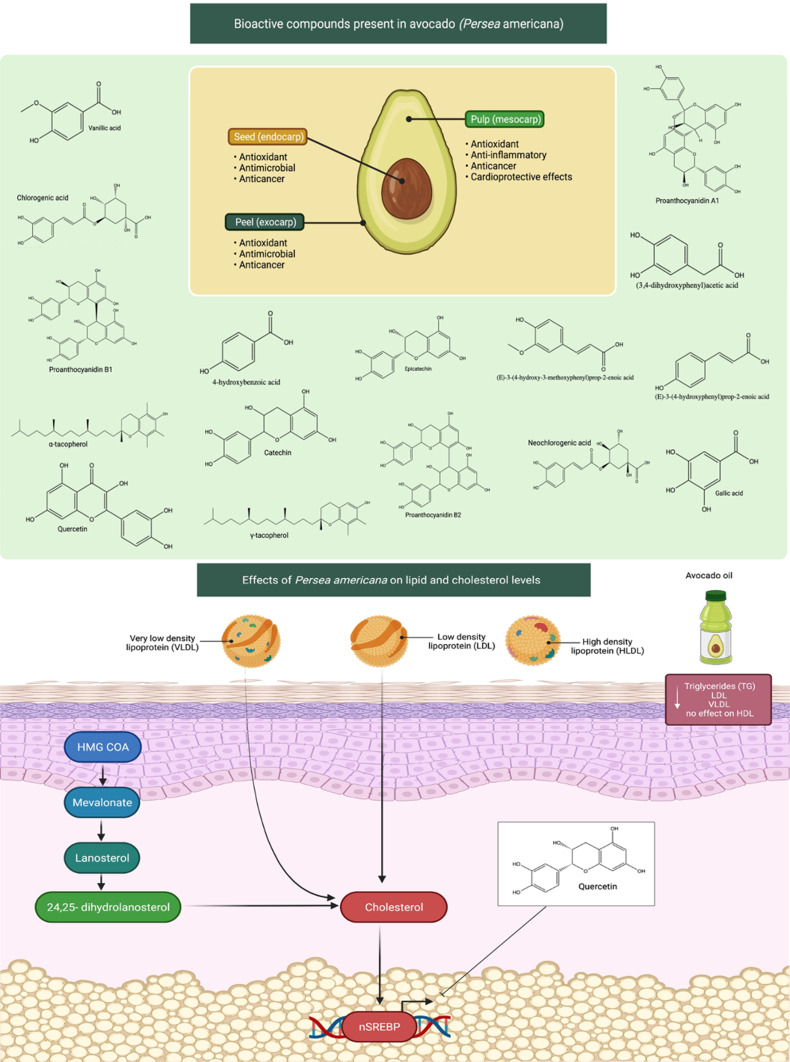
Figure 4.
Bioactive compounds found in avocados (Persea americana) and their influence on lipid and cholesterol levels. Avocados have a wide range of anticancer, antioxidant, and cardioprotective properties, including reducing cholesterol levels, due to the compounds contained in the seed (endocarp), the pulp (mesocarp), and peel (exocarp). Increased lipid and cholesterol levels contributed to the development of heart disease by clogging the arteries with fatty streaks. Avocado fruit and oil consumption reduces blood TG, LDL, VLDL levels. The mechanism of action involves inhibition of cholesterol synthesis. Avocado bioactive components such as quercetin may have the ability to decrease cholesterol levels via modulating HMG-CoA and SREBP.
Abbreviations: TG, triglycerides; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; VLDL, very low-density lipoprotein; HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A; SREBP, sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2.