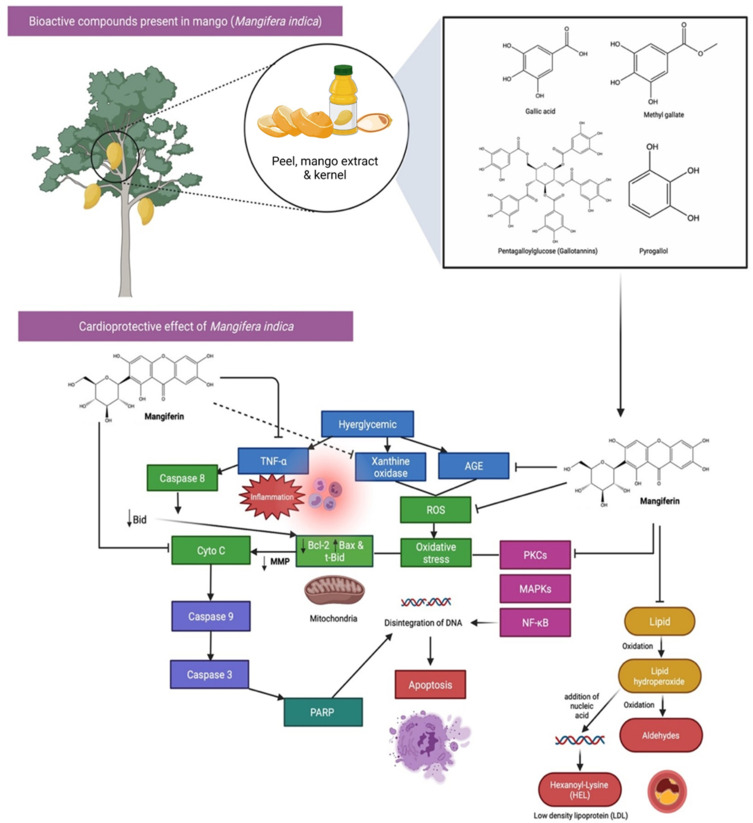
Figure 6.
Bioactive compounds and cardioprotective effects of Mango (Mangifera indica). Mango has a high concentration of well-known bioactive components, such as vitamin C, carotenoids, and polyphenols. The strong oxidative impacts of reactive oxygen species (ROS) have been demonstrated to cause damage to biological molecules (eg, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids) via structural and functional alterations. One of the phenolic compound present, Mangiferin which is highly abundant in Mango, have claimed to be important nutritional antioxidants in preventing and treating several chronic disorders, specifically CVDs by blocking the activation of pro-apoptotic signals, AGE, TNF-α, ROS and lipid peroxidation.
Abbreviations: AGE, advanced glycation end products; TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor α; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; t-Bid truncated Bid; Cyto C, cytochrome complex; poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP); PKCs, protein kinase C isoforms; MAPKs, mitogen-activated protein kinases; NF-kB, nuclear factor kappa B.