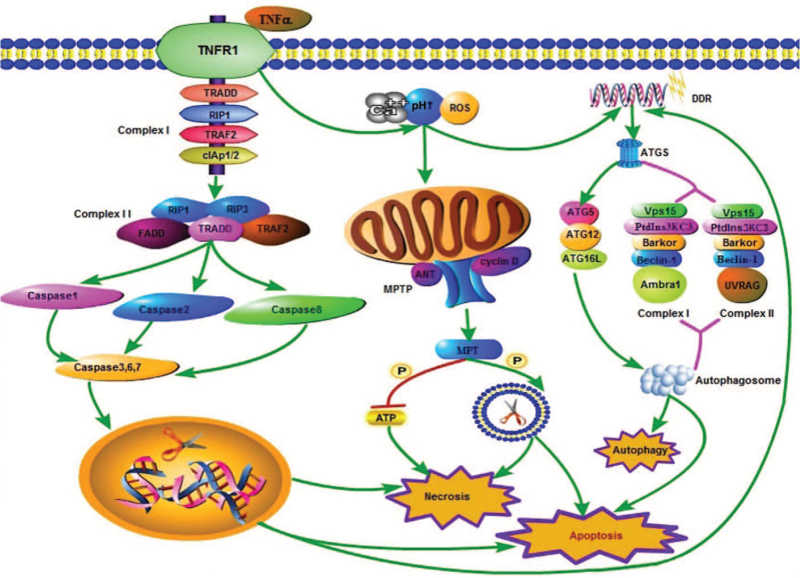
Figure 1.
The mechanisms underlying apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy. In the mitochondrial pathway of necrosis, intracellular and extracellular Ca2+, alkaline pH, and ROS can stimulate the opening of the MPTP (composed of the voltage-dependent anion channel, adenine nuclear translocator [ANT], and cyclin D). Oxidative phosphorylation leads to the cessation of ATP production and destruction of the cell membrane, leading to necrosis. This process can also lead to apoptosis. When the death receptor pathway is triggered, the binding of TNF to TNFR1 leads to exposure of the cytoplasmic death domain of TNFR1, which in turn leads to the recruitment of TRADD. It provides a scaffold for the assembly of complex I (TNFR1, TRADD, RIP1, TRAF2, and cIAP1/2) on the plasma membrane. The complex can promote the formation of complex II (FADD, TRADD, RIP1/3, and TRAF2) under certain conditions. Complex II can mediate the recruitment and activation of caspase-1/2/8, and then activate the downstream caspase-3/6/7. These caspase proteins can destroy DNA in the nucleus, and lead to the destruction of a large number of plasma and cell membranes, thereby leading to necrosis. The activation of caspase proteins, especially caspase-3, is the key factor for triggering apoptosis. DDR induced by various factors leads to the formation of ATGs, such as ATG5 and Beclin-1. ATG5 mediates the formation of the autophagosome through the formation of ATG5–ATG1–ATG16L, while Beclin-1 mediates the formation of the autophagosome through the formation of complex I (composed of Beclin-1, PtdIns3KC3, Vps15, Bakor, and Ambra1) and complex II (composed of Beclin-1, PtdIns3KC3, Vps15, Bakor, and UVRAG), which mediate the formation of autophagosomes, eventually leading to autophagy. The process of apoptosis also depends on the formation of ATGs. ATGs: Autophagy-related proteins; cIAP1/2: Cellular inhibitors of apoptosis 1/2; DDR: DNA damage response; FADD: Fas-associated via death domain; MPTP: Mitochondrial permeability transition pore; PtdIns3KC3: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TNFR1: TNF receptor1; TRADD: TNF-receptor-associated death domain; TRAF2: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptors.