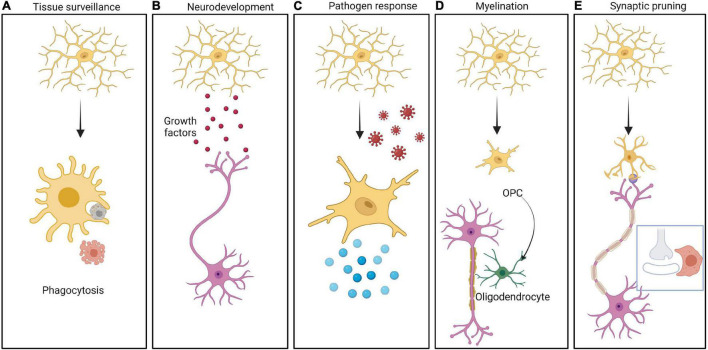
FIGURE 2.
Different roles of Microglia in brain function. The CNS resident innate immune cells, namely microglia can be resting or activated in response to different stimuli. Multiple roles of microglia are depicted in the panels from left to right as follows: (A) Cells undergoing apoptosis in the CNS are cleared by microglia by phagocytosis. (B) Microglia secrete a large variety of growth factors including brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), insulin like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), arginase-1 (Arg-1), nerve growth factor (NGF) etc. These molecules help in neurodevelopment as well as in CNS homeostasis. (C) Microglia serves as a defense against pathogens, by getting activated followed by secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines generating an inflammatory response. (D) Microglia play an important role in myelinating and demyelinating neurons mediated by oligodendrocytes. (E) Microglia takes active part in synaptic pruning by engulfment of synapses in a complement/chemokine mediated manner.