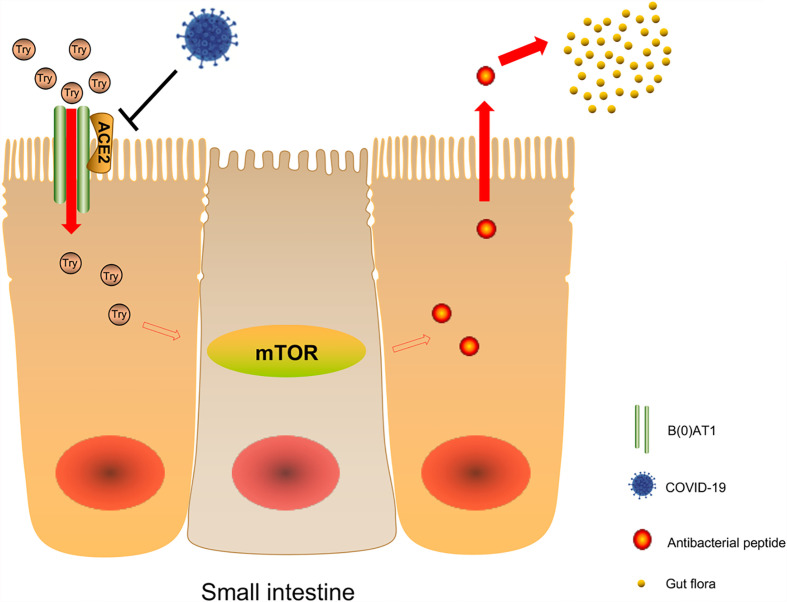
Figure 2.
Possible mechanism of COVID-19 affecting intestinal microbiota. Sodium-dependent neutral amino acid transporter B(0)AT1 is expressed in small intestinal cells and plays an important role in amino acid absorption, while the expression and function of B(0)AT1 depend on the existence of ACE2. After viral infection, the decrease of ACE2 expression will lead to the decrease of B(0)AT1 expression, and dietary tryptophan is mainly absorbed through the B0AT1/ACE2 transport pathway on the surface of the small intestine epithelium, resulting in a significant decrease in plasma tryptophan levels, and lack of tryptophan and its metabolite nicotinamide leads to a decrease in mTOR pathway activity, which affects the expression of antibacterial peptides in the intestinal flora.