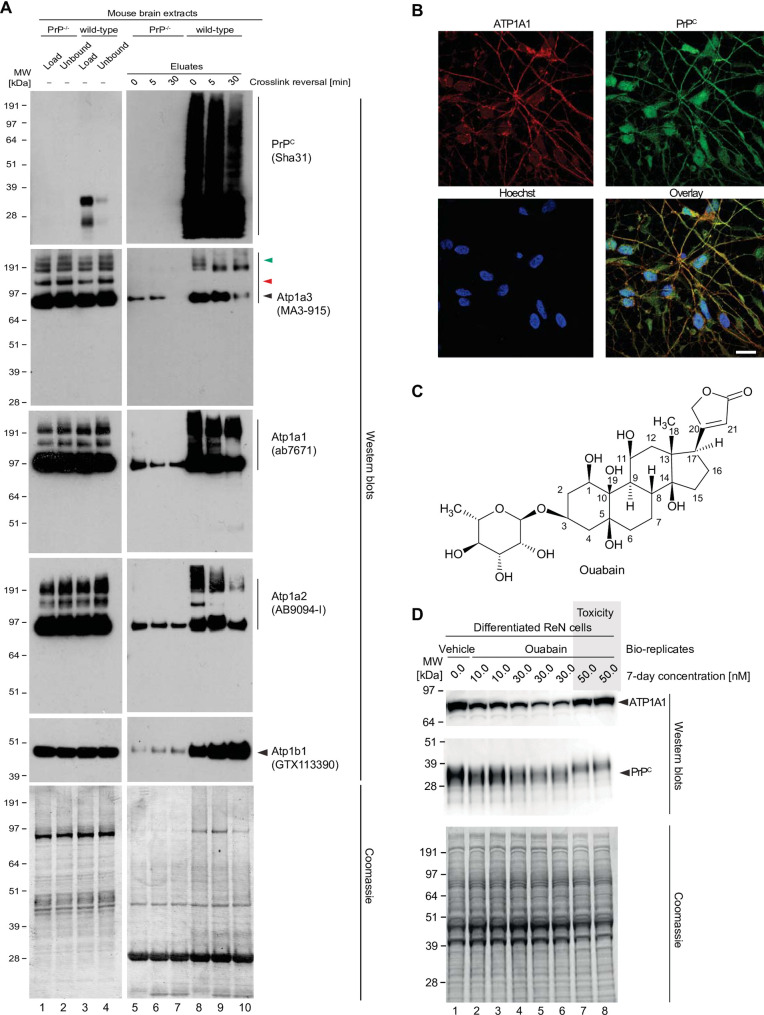
Fig 4. Validation of NKA binding to PrP.
(A) Western blot-based validation of co-immunoprecipitation of NKA subunits with PrP. (B) Evidence of partial cellular co-localization of PrPC and ATP1A1 by co-immunocytochemical analysis of ReN VM cells, with Hoechst stain serving as the nuclear counter stain. Scale bar: 10 nm. (C) Chemical structure of the NKA inhibitor ouabain. (D) Parallel ouabain concentration-dependent effects on NKA and PrPC levels. Exposure of differentiated ReN VM cells to ouabain at concentrations up to 50 nM causes a biphasic effect on PrPC and ATP1A1 levels, with concentrations up to 30 nM leading to a ouabain concentration-dependent reduction in steady-state levels of both proteins, and exposure to 50 nM provoking a reproducible slowing of PrPC during SDS-PAGE separation that parallels an increase in steady-state ATP1A1 levels.