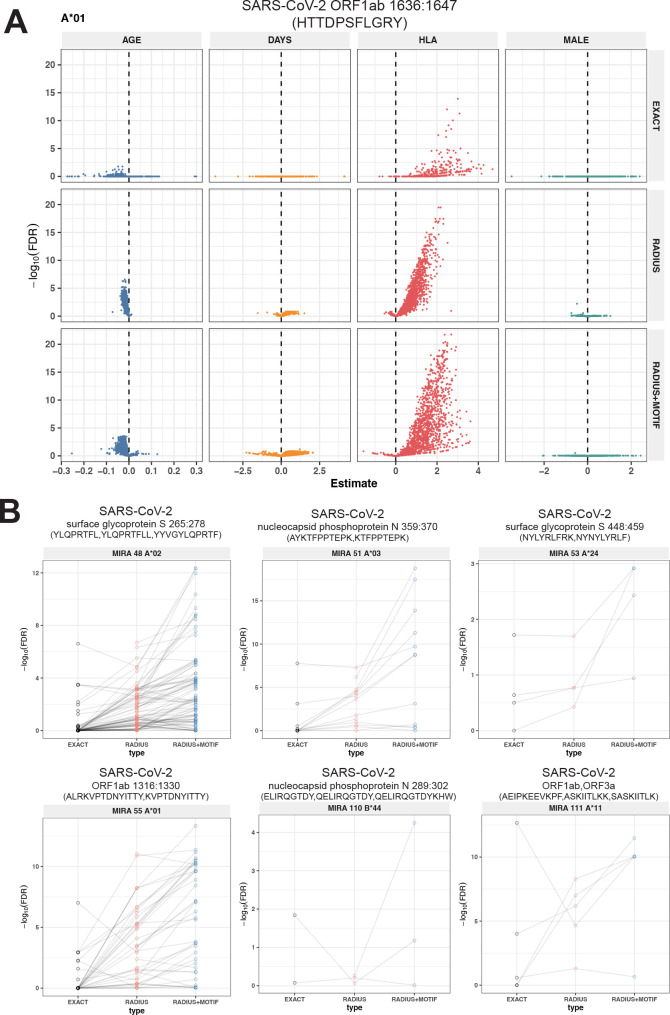
Figure 9. Associations of T-cell receptor (TCR) features with participant age, days postdiagnosis, HLA genotype, and sex in TCR β-chain repertoires of COVID-19 patients (n = 694).
(A) Beta-binomial regression coefficient estimates (x-axis) and negative log10 false discovery rates (y-axis) for features developed from CD8+ TCRs activated by SARS-CoV-2 MIRA55 ORF1ab amino acids 1636:1647, HTTDPSFLGRY. The abundances of meta-clonotype conformant TCRs are more robustly associated with predicted HLA type than for exact clonotypes. (B) Signal strength indicating a positive association between the HLA genotype (two-digit) with TCR β-chain clonotypes (EXACT) and meta-clonotype conformant TCRs (RADIUS or RADIUS + MOTIF), where the restricting HLA genotype was inferred from independent data: (i) MIRA48, (ii) MIRA51, (iii) MIRA53, (iv) MIRA55, (v) MIRA110, and (vi) MIRA111 (Supplementary file 1f). Each set of three symbols connected by a line represents an evaluation TCRs conformant to an individual clonotype or a meta-clonotype. Models were estimated with counts of productive TCRs matching a clonotype (EXACT) or conforming to a meta-clonotype (RADIUS or RADIUS + MOTIF) with the following definitions: (1) EXACT (inclusion of TCRs matching the centroid TRBV gene and amino acid sequence of the complementarity determining region [CDR]3), (2) RADIUS (inclusion criteria defined by a TCR centroid and optimized TCRdist radius), and (3) RADIUS + MOTIF (inclusion criteria defined by TCR centroid, optimized radius, and CDR3 motif constraint). See Methods for details. Meta-clonotype radii were engineered using synthesized backgrounds developed for each MIRA set. Each background contained 100,000 Optimized Likelihood estimate of Immunoglobulin Amino acid sequences (OLGA)-generated TCRs and 100,000 TCRs subsampled from umbilical cord blood; OLGA-generated TCRs were sampled to match to the V–J gene frequency in each MIRA receptor set (i.e., MIRA1, 48, 51, 53, 55, 110, or 111) with weighting to account for the sampling bias (see Methods for details).