Figure 1.
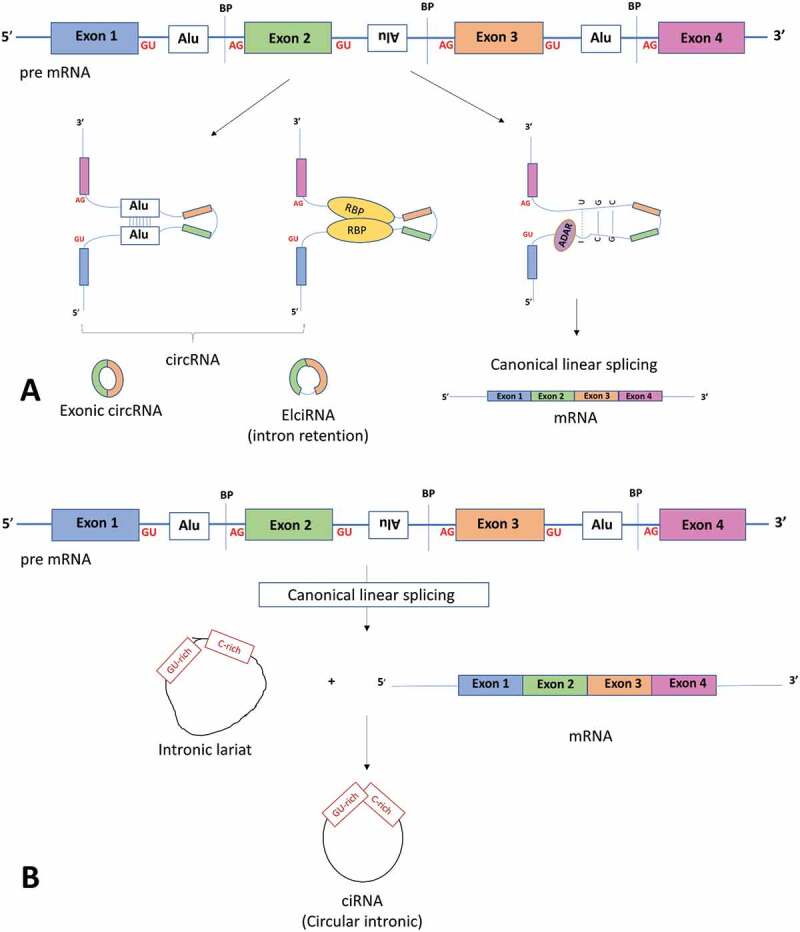
Components involved with linear mRNA or circular RNA biogenesis. (a) The top panel shows a pre-mRNA transcript with four exons. Long flanking introns containing inverted repeat elements such as Alu elements or trans-acting RBP proteins bring the downstream splice site into close proximity with the upstream splice site to favour back splicing and thus circRNA production. Conversely, introns bound by ADAR1 ‘melt’ RNA secondary structures by disrupting intronic base pairing to disrupt circularization. (b) Intronic circRNA biogenesis: Linear splicing produces lariat structures that are usually debranched and hydrolysed. However, GU rich and C rich intronic motifs escape debranching to form ciRNAs (intronic circRNAs). ADAR adenosine deaminases acting on RNA, BP: Branch points. RBP: RNA binding proteins. ALU: Alu repeat elements, mRNA messenger RNA
