Figure 4.
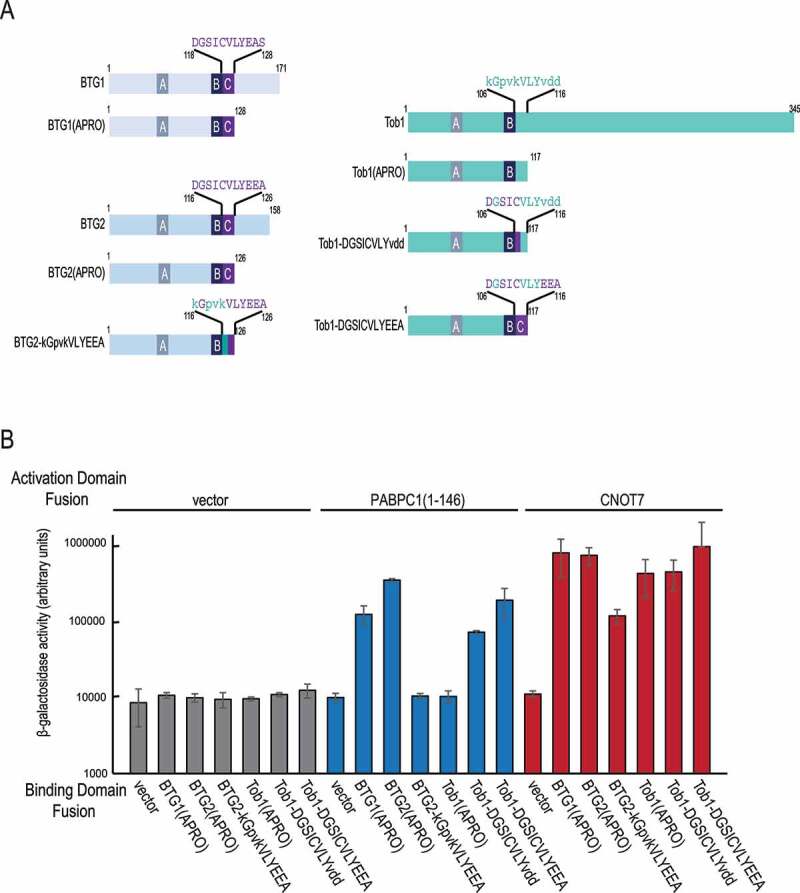
The boxC motif is sufficient and necessary to allow binding to PABPC1
A) Schematic representation of human BTG1, BTG2 and Tob1 proteins and mutation introduced. The conserved boxA (A) and boxB (B) motifs, signatures for the BTG/Tob family are indicated. The sequences mutagenized, overlapping the 11 amino acid boxC motif specific for BTG1 and BTG2, are presented with colour code: amino acids of the boxC motif are in purple, while equivalent residues in Tob1 are in green. To facilitate the identification of substituted positions, uppercase letters indicate residues present in BTG2 boxC, while lowercases correspond to amino acids specific for Tob1. B) Interaction of wild-type and mutant BTG1, BTG2, and Tob1 APRO domains with CNOT7 and the first part of the PABPC1 multi-RRM domain in yeast 2-hybrid assay. The Y187/L40 yeast strain was co-transformed with plasmids expressing the indicated LexA-Binding-Domain and Gal4-Activating-Domain fusion proteins. Interaction between the different chimeric proteins indicated was assessed by β-galactosidase assays performed in duplicates. Activities are expressed in arbitrary units and plotted on a logarithmic scale. Three biological replicates were assayed and the corresponding standard deviations plotted as error bars.
