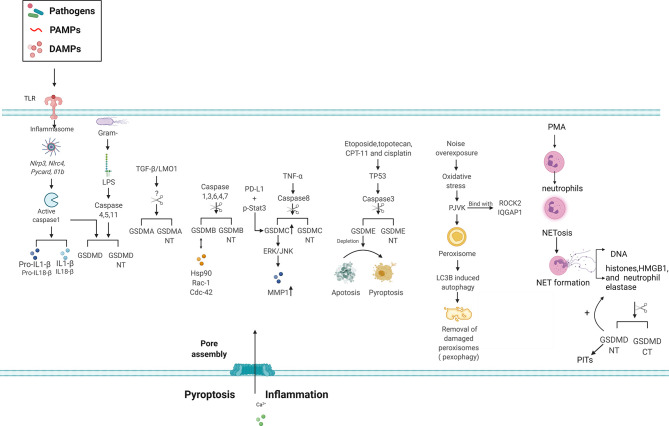
Figure 3.
Signaling pathways of GSDM family members in inflammasome signaling, pore formation and cell death. GSDMD is involved in pyroptosis via canonical and non-canonical inflammasome mediated pathways following cleavage by inflammatory caspases. The N-terminal domain of GSDMA-E can bind with membrane lipids of the plasma membrane and form pores, allowing release of the inflammatory cytokines IL-1BIL-1B and IL-18 and induction of pyroptosis. However, the inflammatory caspase responsible for GSDMA cleavage remain elusive. Various stimuli and upstream signals like PD-L1, TP53 and TNF-α, can lead to GSDMs cleavage and subsequent cell death. GSDMs are able to bind with other molecules, such as Hsp90, Rac-1 and ROCK2, and the following function require further investigation. Alternatively, depletion of GSDME can switch apoptosis to pyroptosis in cells. The ability of PJVK to bind membrane lipids or form pores in the plasma membrane is uncertain, however it is implicated autophagy related pexophagy. In addition, GSDMD leads NETosis as the key effector GSDMD is cleaved by neutrophil elastase during NETosis induced by classic stimulants such as PMA, releasing the active GSDMD-N.GSDMD-N, Gasdermin N-terminal; GSDMA, Gasdermin A; GSDMB, Gasdermin B; GSDMC, Gasdermin C; GSDMD, Gasdermin D; GSDME, Gasdermin E; HSP90, heat shock protein 90; IL-1BIL-1B, interleukin-1β; IL-18, interleukin-18; PJVK, Pejvakin; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand1; ROCK2, rho associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 2; Rac-1, ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1; Cdc42, cell division cycle 42; IQGAP1, IQ Motif Containing GTPase Activating Protein 1; MMP1, Matrix Metallopeptidase 1; ERK, extracellular regulated protein kinase; JNK,c-Jun N-terminal kinase; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; LOM1, LIM Domain Only 1; PMA,phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate; Netosis, neutrophil extracellular trap formation (NETosis); PITs: pore induced intracellular pits.