Figure 1.
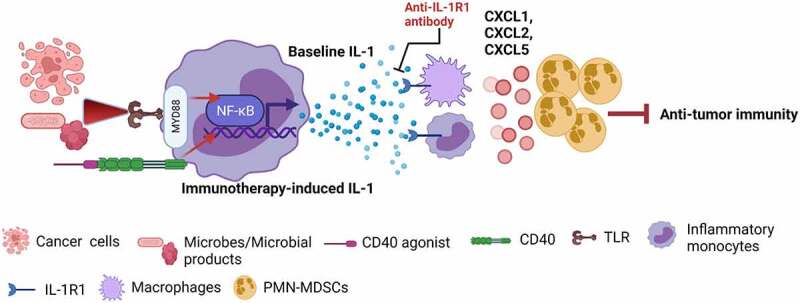
Baseline and immunotherapy-driven IL-1 suppresses anticancer immunity. Activation of the TLR–NF-kB pathway through necrotic cancer cells or microbes/microbial products induces baseline IL-1 production by inflammatory monocytes, and activation of the CD40–NF-kB pathway through CD40 agonist induces immunotherapy-driven IL-1 production by inflammatory monocytes. In response to IL-1, IL-1R1-expressing monocytes and macrophages produce PMN-MDSC-recruiting chemokines (CXCL1, CXCL2, and CXCL5), leading to PMN-MDSC trafficking into tumors and PMN-MDSC-mediated suppression of anti-tumor immunity. These consequences make tumors resistant to immunotherapy. Blocking the IL-1 signaling pathway by anti-IL-1R1 antibody overcome IL-1-mediated resistance to immunotherapies by stopping the PMN-MDSC trafficking into the tumor microenvironment (Created with BioRender.com)
IL-1: interleukin-1; IL-1R1: IL-1 receptor type 1; MyD88: myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88; NF-κB: nuclear factor-kappa B; TLR: toll-like receptor; PMN-MDSCs: polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressive cells
