Figure 6.
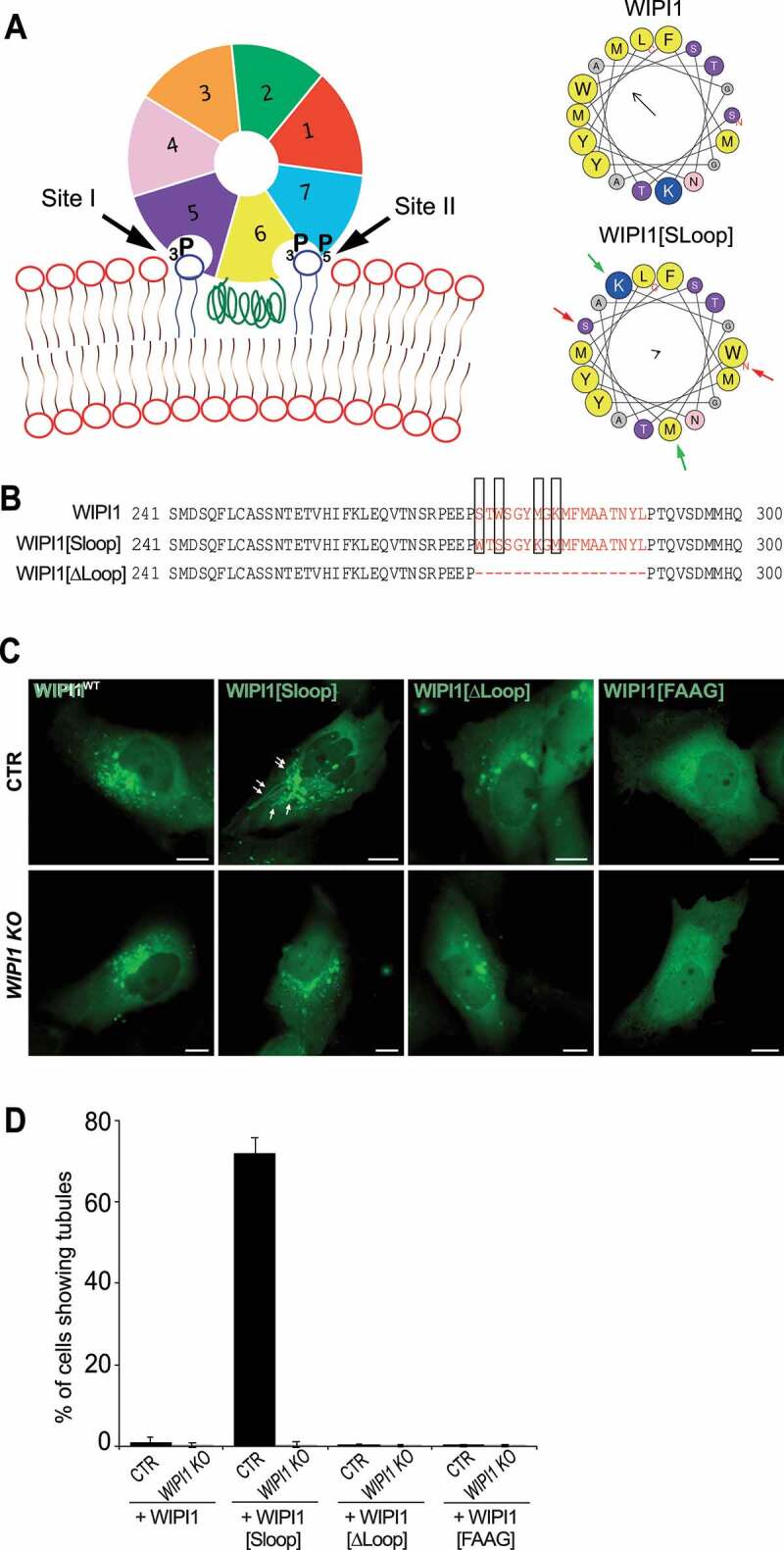
Role of the amphipathic α-helix in blade 6 of WIPI1. (A) Schematic depiction of WIPI1, showing its 7-bladed ß-propeller, the two phosphoinositide binding sites and the hydrophobic CD-loop on blade 6 that folds into an amphipathic helix when in contact with a bilayer [55]. Helical wheel projections show the CD-loop on blade 6 of WIPI1 and WIPI1[Sloop]. Colored arrows indicate the two pairs of amino acids that have been swapped. The magnitude and direction of the hydrophobic moment of the helices was predicted using the online tool Heliquest [118]. It is indicated by the vector in the center of the wheels. (B) Sequences of the hydrophobic loop regions of WIPI1, WIPI1[Sloop] and WIPI1[ΔLoop]. The amino acids removed in WIPI1[ΔLoop] were EEPSTWSGYMGKMFMAATNYL, which comprises the entire sequence shown in the helical wheels. Predicted α-helices analyzed in (A) are plotted in red. The two pairs of hydrophobic/hydrophilic amino acids swapped in WIPI1[Sloop] are highlighted by rectangles. (C) Representative images of CTR and WIPI1 KO cells expressing EGFP-tagged wild-type or the indicated mutant forms of WIPI1. Pictures were taken 18 h after transfection. Tubules are marked by arrows. Scale bar: 10 μm. (D) Quantification of control and WIPI1 KO cells showing tubules after expressing different WIPI1 plasmids for 18 h. The data are mean values ±s.d.; n = 3 independent experiments (20 transfected cells were analyzed per plasmid per experiment in both CTR and WIPI1 KO cells)
