Figure 6.
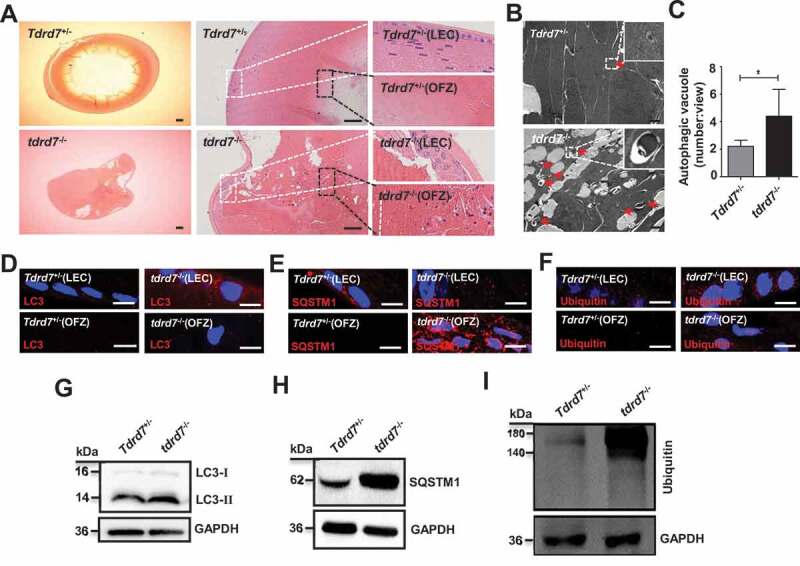
Evaluation of ocular tissues in Tdrd7+/− and tdrd7−/− mice. (A) H&E staining of lenses showed atrophic lens structure in tdrd7−/− mice. There are a number of bubbles in lens epithelial cells (LEC) and lens fiber cells, and degenerative nuclei in the organelle-free zone (OFZ). White box: LECs, black box: OFZ. Scale bar: 200 μm. (B) Detection of Tdrd7+/− and tdrd7−/- mice lenses using TEM. The red arrows indicate the autophagic vacuoles. (C) Quantification of the average number of autophagic vacuoles in Tdrd7+/− and tdrd7−/− mice lenses using TEM analysis. *P < 0.05. (D-F) Immunostaining of Tdrd7+/− mice lenses for LC3 (D), SQSTM1 (E) and ubiquitin (F) (red signal) revealed the presence of LC3-II, SQSTM1, and ubiquitin in LECs without any staining present in the OFZ. By contrast, immunostaining of tdrd7−/− mice lenses revealed accumulation of LC3-II, SQSTM1, and ubiquitin in LECs and the OFZ of tdrd7−/− mice lenses. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue signal). Scale bar: 10 µm. (G-I) Immunoblotting analysis of Tdrd7+/− and tdrd7−/− mice lenses for LC3 (G), SQSTM1 (H), and ubiquitin (I) confirmed the accumulation of LC3-II, SQSTM1, and ubiquitin in tdrd7−/− mice lenses
