Figure 12.
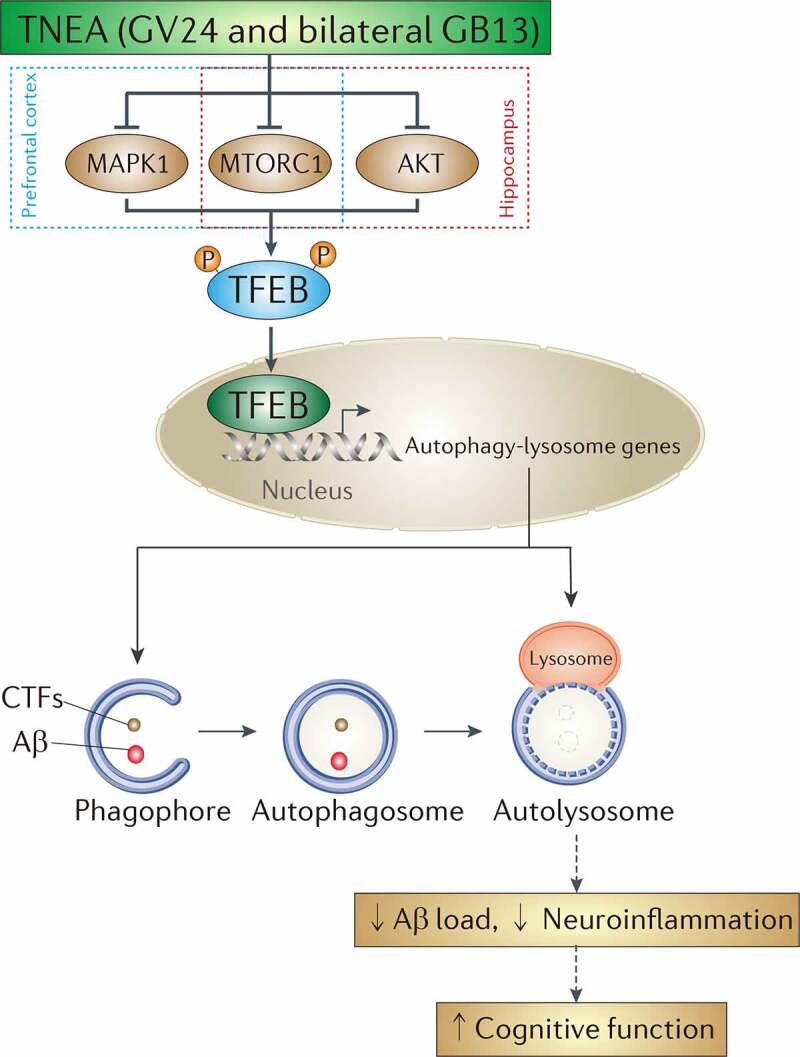
A mechanistic model showed that TNEA attenuates cognitive impairment in AD involving the activation of TFEB. EA (GV24 and bilateral GB13) treatment inhibits MTORC1 and MAPK1 in the prefrontal cortex, and inhibits MTORC1 and AKT in the hippocampus respectively, thus promoting the dephosphorylation and nuclear translocation and of TFEB to transcriptionally upregulate the autophagy-lysosomal pathway, which is essential for the degradation of Aβ and carboxy-terminal fragments (CTFs)
