Figure 4.
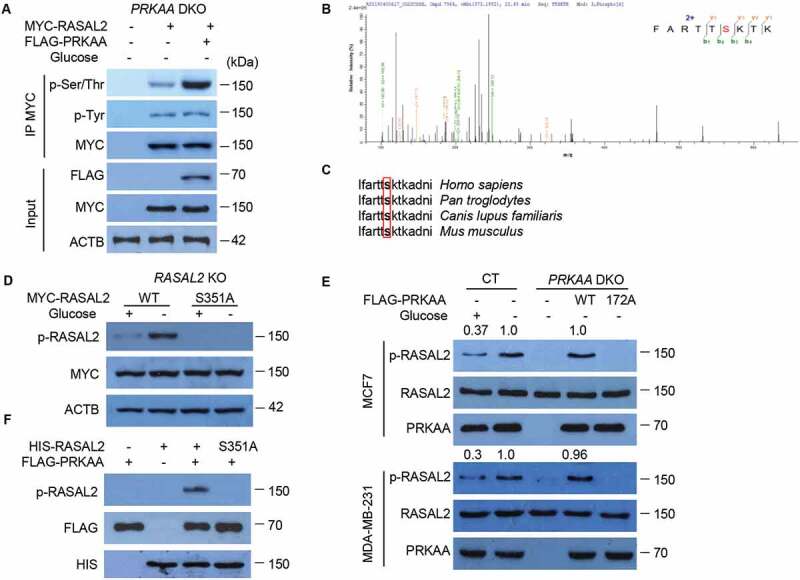
PRKAA phosphorylates RASAL2 at S351. (A) PRKAA-DKO MCF7 cells co-transfected MYC-RASAL2 with or without FLAG-PRKAA were cultured in the glucose-starvation medium for 4 h. The co-IP analyses were performed by using anti-MYC beads. (B) Identification of phosphorylation site(S) on RASAL2 by mass spectrometry. Immunoprecipitations of MYC-RASAL2 from the lysates of PRKAA-DKO MCF7 cells co-transfected MYC-RASAL2 with FLAG-PRKAA as generated in (A) were used for mass spectrometry analysis. The results showed a tryptic peptide (FARTTpSKTKAD) from FLAG-PRKAA treated RASAL2 protein with a mass shift of +79.9663 Da at the serine residue. The results suggested that S351 was phosphorylated. (C) S351 in human RASAL2 protein is evolutionally conserved in different species. S351 residues in the box are highlighted in bold. (D) RASAL2-KO MCF7 cells transfected with indicated RASAL2 constructs were incubated with or without glucose deprivation for 4 h. The cell lysates were used for immunoblotting as indicated. (E) MCF7 or MDA-MB-231 cells with or without PRKAA DKO and reconstituted expression of FLAG-PRKAA (WT or T172A) were cultured in the presence or absence of glucose starvation medium for 4 h. The cell lysates were used for immunoblotting as indicated. The relative amount of p-S351 RASAL2 was semi-quantified by grayscale analysis. (F) PRKAA phosphorylates RASAL2 in vitro. In vitro kinase assay carried out with purified HIS-RASAL2 or HIS-RASAL2S351A, purified activated-FLAG-PRKAA complex prepared from 293 T cells expressing FLAG-PRKAA after glucose starvation for 4 h and nonradioactive ATP, and mixed in the reaction buffer for 20 min at 30°C. Immunoblotting analyses were performed with the indicated antibodies
