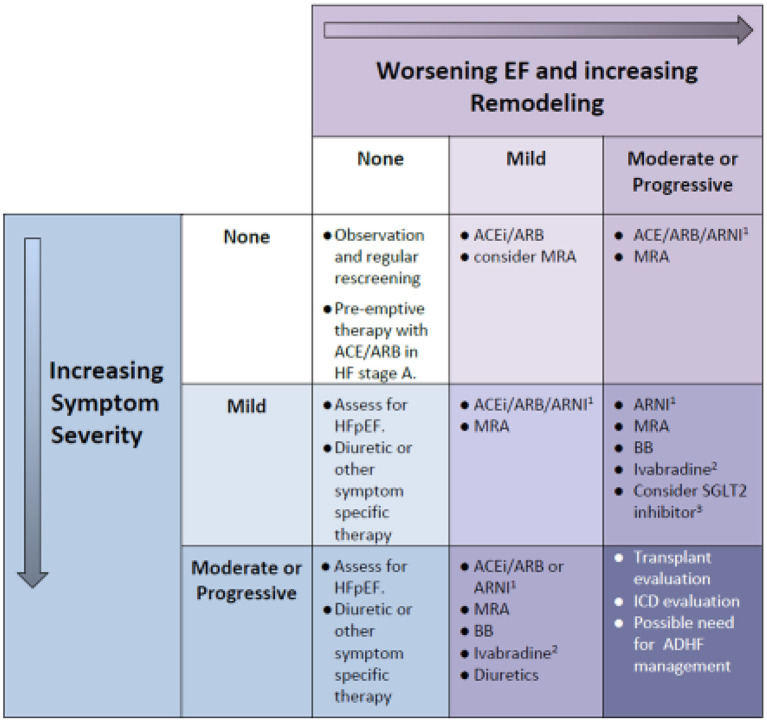
Figure 3.
Which Drug for Which Patient: a simplified intuitive guide to the assignment of medical treatment in chronic HF. Remodeling severity is portrayed on the horizontal axis, with increasingly severe symptoms on the vertical axis. Note that progressive symptoms in the absence of LV dilation implies restrictive diastolic function (a form of HFpEF), which may be refractory to management and also require assessment for cardiac transplant and/or ICD. When symptoms are severe and remodeling is advanced (lower right cell) we revert to acute decompensated heart failure management. All patients require an expert assessment and a tailored approach to management depending on the etiology of HF, the severity of decline in EF and degree of LV remodeling (LV dilation). 1Indications exist in adults, and use in children is FDA approved, although the outcome of a clinical trial in children is still awaited. 2Indication is based on a phase II clinical trial in children, with FDA approval given for children over 6 m age. 3Class IIa indication in adults with HFrEF. ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARNI, angiotensin receptor blocker/neprilysin inhibitor; BB, beta blocker; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved EF; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; SGLT-2, sodium glucose co-transporter protein 2.