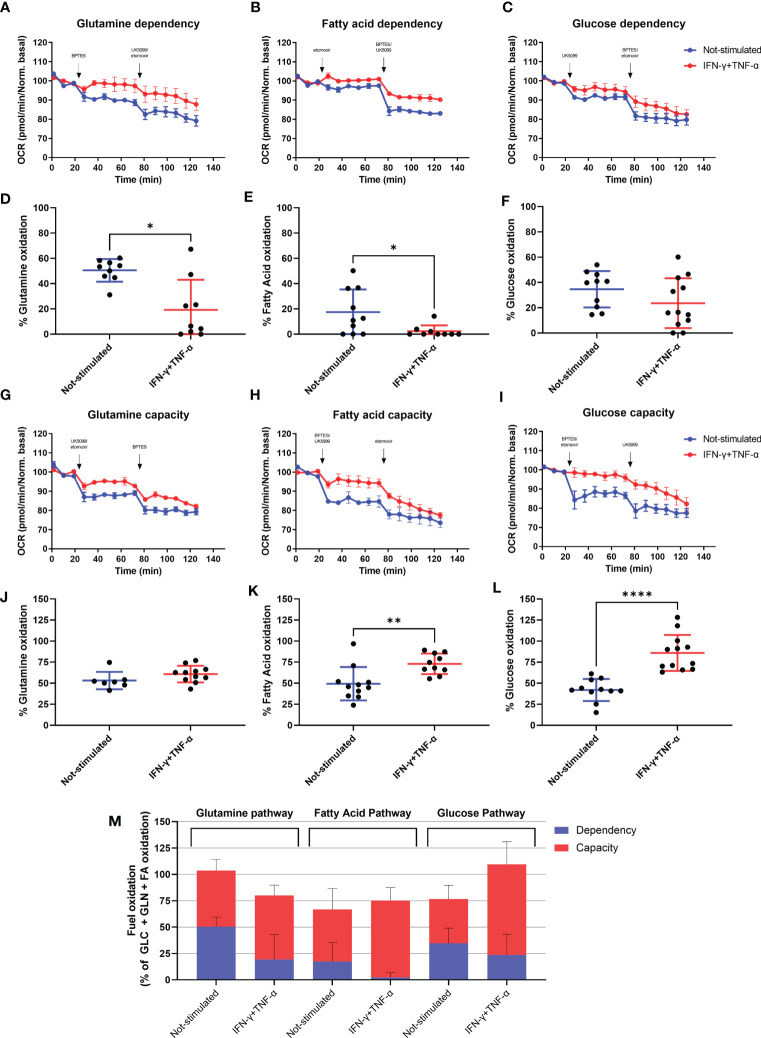
Figure 6.
Assessment of AC-16 fuel oxidation in response to IFN-γ and TNF-α stimulation. Oxygen consumption rate of 48h IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) and TNF-α (5 ng/ml)-stimulated AC-16 cells was obtained in Seahorse XFe24 Analyzer. Arrows show injection of inhibitors (combined or not) of molecules specific to different fuel oxidation pathways, such as; BPTES, inhibitor of glutaminase GLS1 (KGA, glutamine pathway), etomoxir, inhibitor of carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1 (CPT-1, fatty acid pathway) and UK5099, inhibitor of the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC, glucose pathway). (A–F) OCR dependency of glutamine, fatty acid oxidation and glucose. (G–L) OCR capacity of glutamine, fatty acid oxidation and glucose. (M) Global fuel oxidation. Standard error of the mean in line graphs. Standard deviation is from ≥9 independent measurements. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001 Mann-Whitney test.