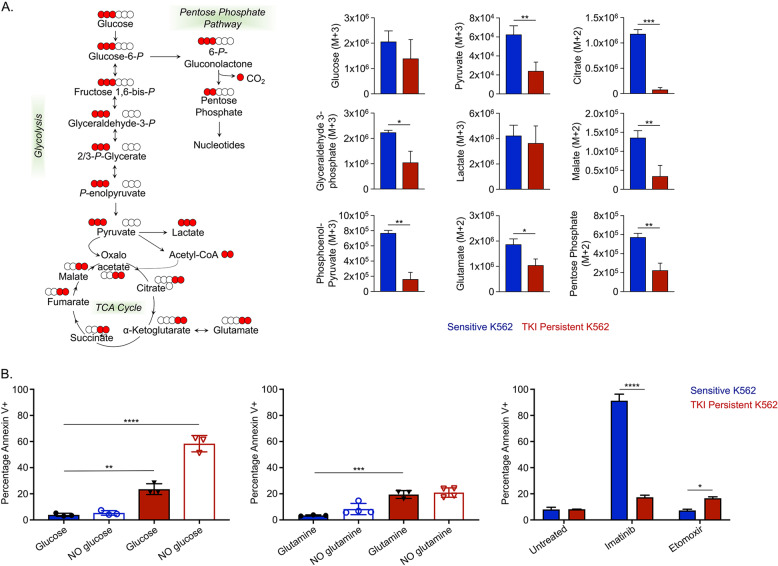
Fig. 5. TKI-persistent K562 have an active glycolysis and increased fatty acid accumulation.
A Unit area plots for metabolites labeled in glycolysis, citric acid cycle and PPP post 3 h incubation of 200,000 sensitive and IM-persistent K562 with isotopically labeled 13C1,2,3-glucose. The metabolites were measured with UHPLC-MS. B Sensitive and IM-persistent K562 treated with 1 µM Imatinib were starved with glucose (right) or glutamine (middle) for 48 h or treated with 10 µM Etomoxir for 3 days. Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry using annexinV apoptosis assay. The data are representative mean ± SD from two independent experiments. Unpaired student t test or Two-way ANOVA was used to determine statistical significance with Tukey’s multiple comparison. p values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001; ns = not significant.