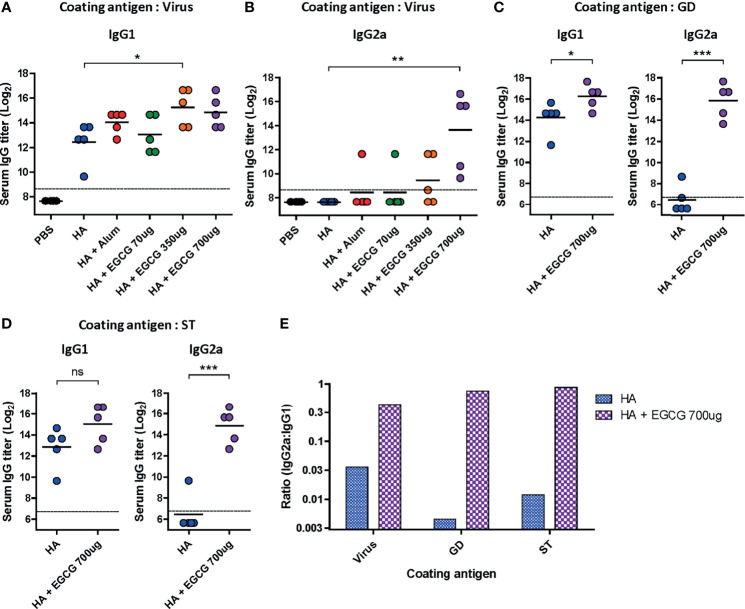
Figure 4.
Characterization of serum IgG antibody subclass elicited by EGCG-adjuvanted HA vaccine. PBS or 7 µg of HA antigens with or without adjuvant (30 μL of alum or 70, 350, or 700 μg of EGCG) were injected into mice via IM route thrice every 2 weeks. Sera were collected 2 weeks after the last vaccination. (A, B) IgG1 (A) and IgG2a (B) antibody responses to influenza PR8 virus. The antibody titer of each sample was expressed as the endpoint dilution with an absorbance value 2× greater than that of the PBS control group. Data were log-transformed and expressed as means (horizontal lines) and scatter plots. The detection limits (dashed lines) were 400. (C, D) IgG1 and IgG2a antibody responses to GD (C) or ST (D) of HA protein of influenza PR8 virus. Data were log-transformed and expressed as means (horizontal lines) and scatter plots. The detection limits (dashed lines) were 100. (E) IgG2a/IgG1 ratios of HA and EGCG-adjuvanted HA. The bar graphs indicate geometric means. For convenience, the IgG2a/IgG1 ratios were shown as log scale; corresponding to 12 fold (virus), 190 fold (GD), and 72 fold increase (ST) by EGCG. Student’s t-test was used to compare two different groups. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test was conducted to compare three or more groups (***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05. ns, not significant).