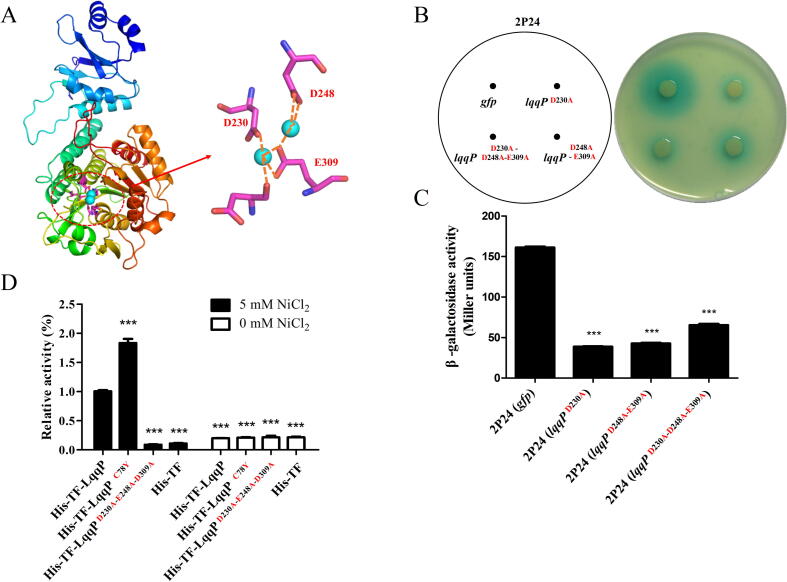
Fig. 3.
The enzyme activity of LqqP does not seem to be related to its block of AHL production in P. fluorescens 2P24. (A) Homologous modeling of LqqP. The three key residues required for LqqP enzyme activity were predicted and highlighted in red. (B-C) The role of LqqP variants in blocking amount of AHL produced by 2P24. The coding regions of LqqP variants shown in red was expressed in 2P24 and the AHL production was detected in plates (B). (C) AHL quantification shown in panel B. The average data from three experiments is presented, ± SD. ***P < 0.0001 relative to 2P24 expressing gfp. (D) The enzyme activity of LqqP and its derivatives shown in red. LqqP and its variant genes were expressed with N-terminal fused His- and- TF tags. His-TF is served as a negative tag, in which TF is a trigger factor and a prokaryotic ribosomal binding partner protein that can induce co-translational folding of new peptide chains. Average data from three experiments is shown, ± SD. ***P < 0.0001 relative to His-TF-LqqP. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)