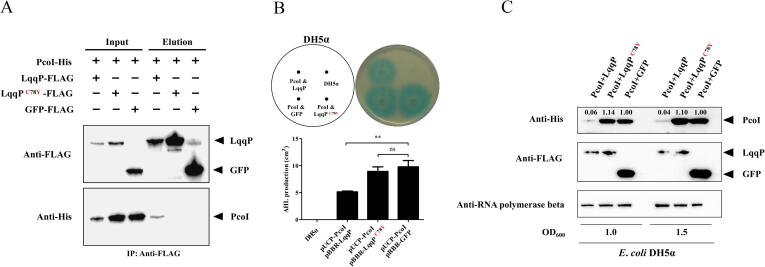
Fig. 6.
C78 is essential for both the LqqP-PcoI binding and LqqP functioning in E. coli DH5α. (A) Co-IP reveals that C78 is required for LqqP-PcoI binding. The plasmids pBBR-LqqP and pUCP26-PcoI were co-transformed into E. coli DH5α. Immunoprecipitation was performed using anti-FLAG antibody. Western blot was performed by using anti-FLAG and anti-His antibodies. (B) The effect of the expression of native LqqP and its derivative LqqPC78Y gene on the production of PcoI-dependent AHL in E. coli DH5α. The AHL production and its quantification in the plates are displayed in the upper and lower panels, respectively. AHL production is calculated by dividing the area of the blue circle by the area of the colony. (C) The effect of co-expression of LqqP or its derivative LqqPC78Y gene on the abundance of PcoI in E. coli DH5α. The average data from three experiments is presented, ± SD. **P < 0.01. The band intensities were quantified and analyzed using ImageJ (https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/), with numbers representing the relative intensities of the corresponding bands. The intensity levels of the bands in lane “PcoI-GFP” were set to 1.00. “ns” stands for not statistically significant. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)