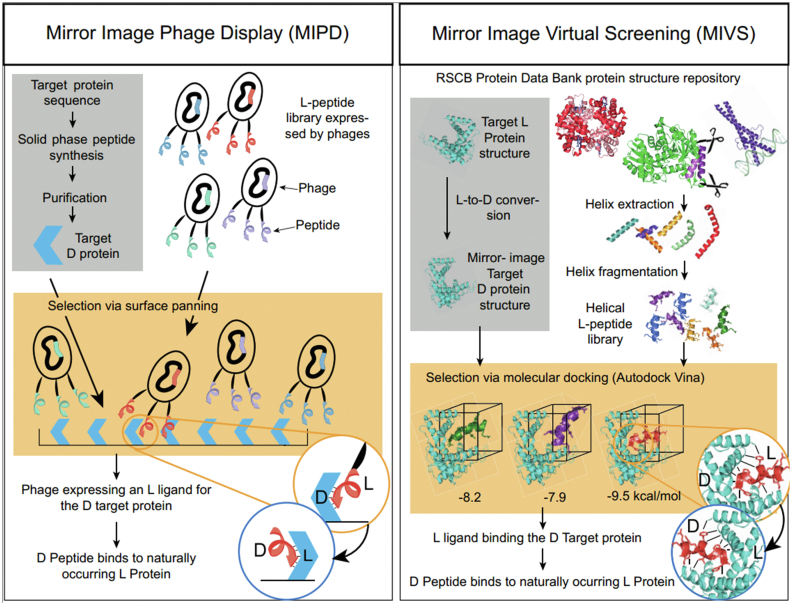
Fig. 3.
Schematic representation of the MIPD and MIVS workflow. MIPD: A library of random L-peptides expressed on the surface of bacteriophages is selected via surface panning against a chemically synthesized D-analogue of the target L-protein. MIVS: A structural library of helical L-peptide segments extracted from the PDB is screened for binding affinity towards an in silico mirrored D-version of the target L-protein structure via molecular docking. Both methods yield L-peptide ligands to D-protein targets. Consequently, the corresponding D-peptides bind to the naturally occurring L-protein target (see Fig. 1).